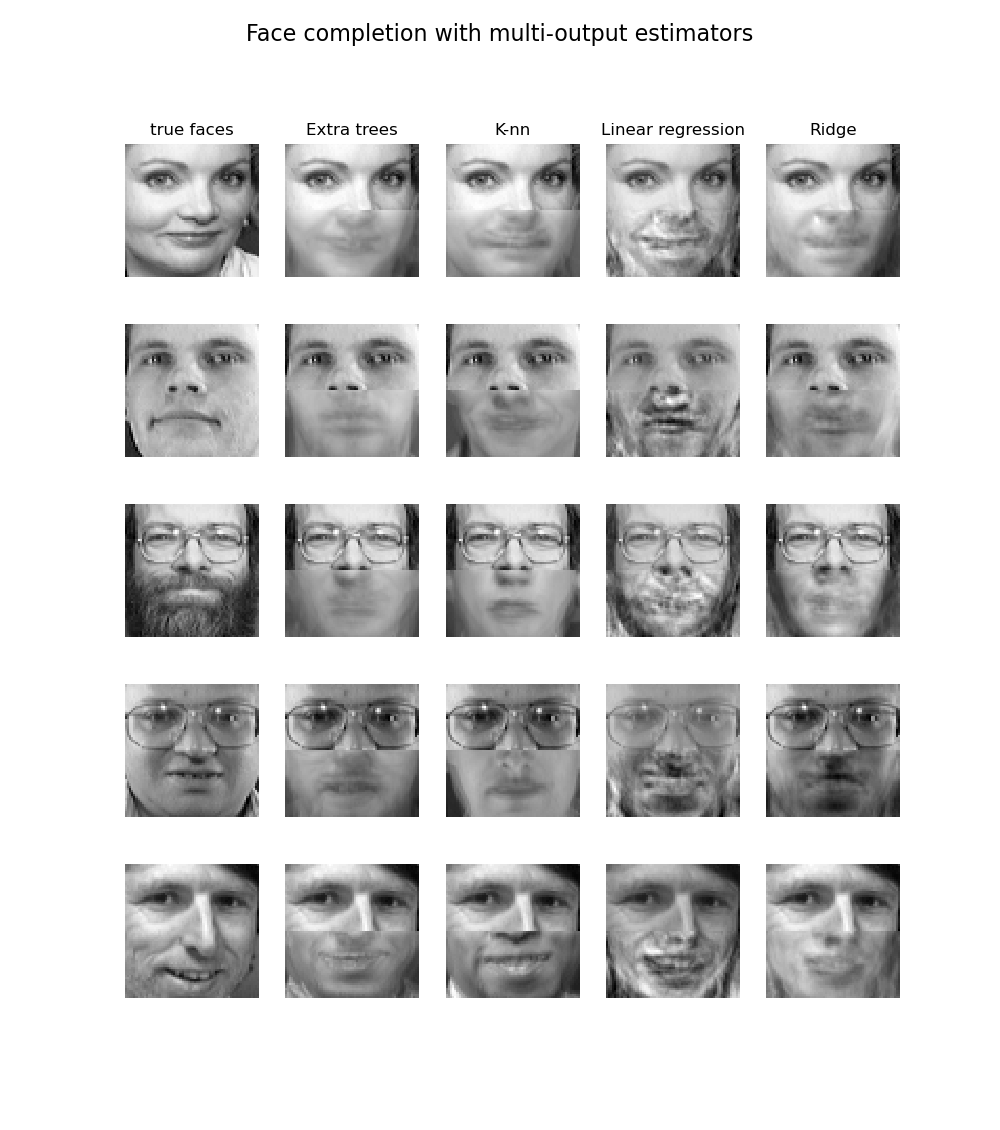
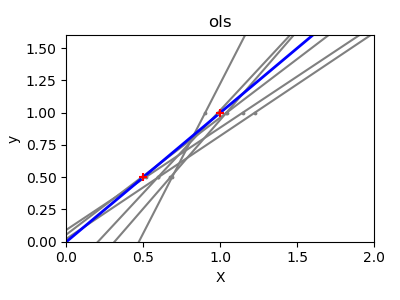
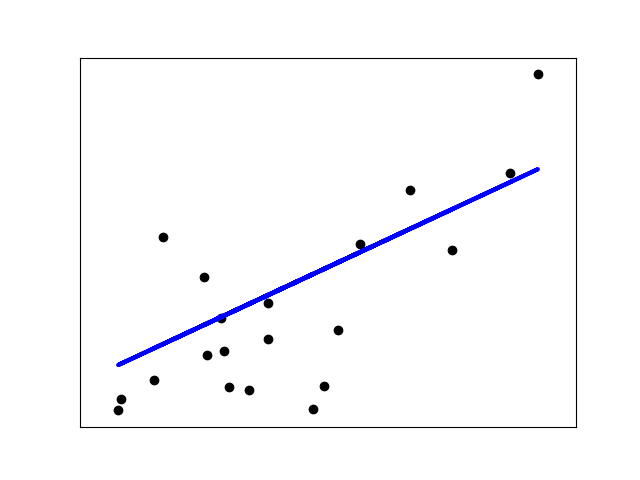
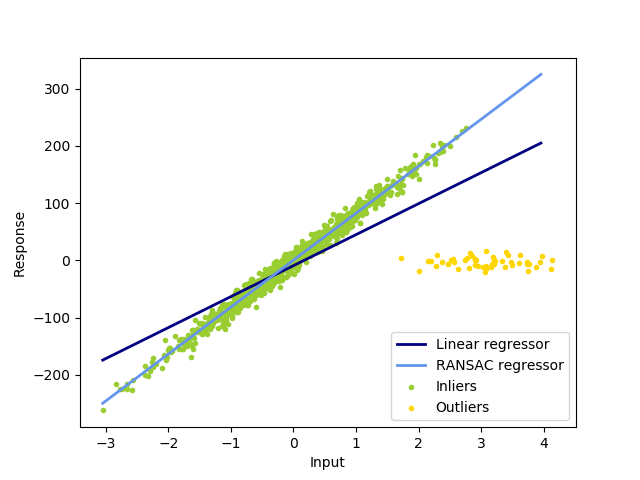
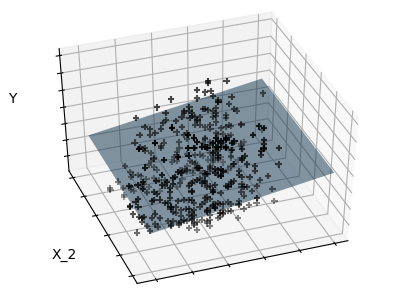
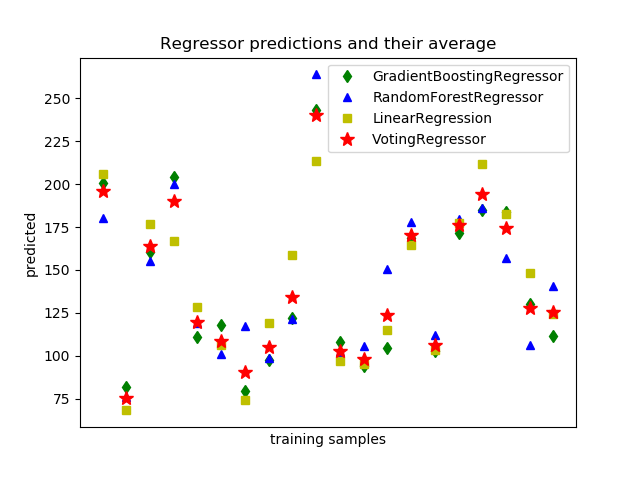
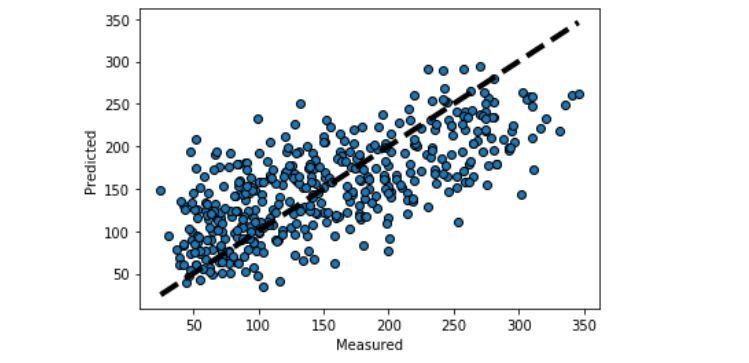
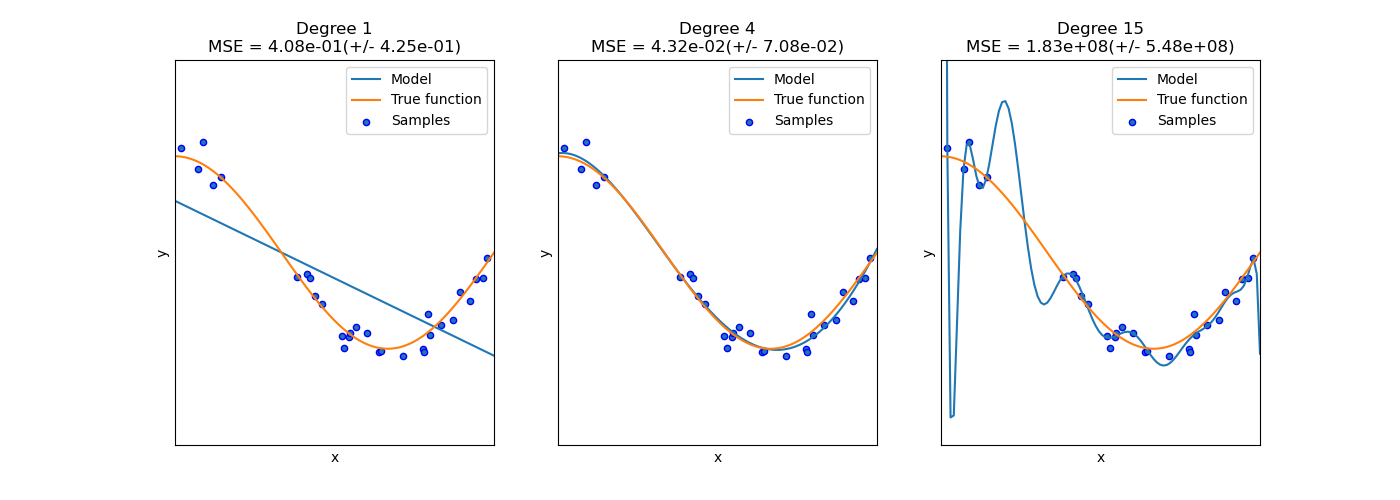
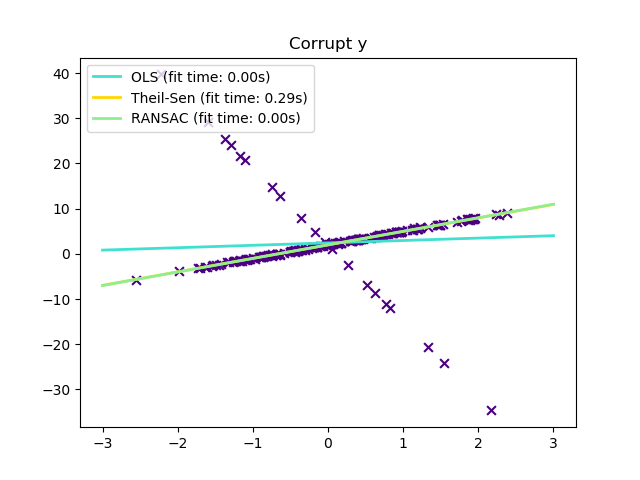
sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression¶
class sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression(*, fit_intercept=True, normalize=False, copy_X=True, n_jobs=None)
普通最小二乘线性回归。
LinearRegression使用系数w =(w1,…,wp)拟合线性模型,以最小化数据集中实际目标值与通过线性逼近预测的目标之间的残差平方和。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| fit_intercept | bool, default=True 是否计算此模型的截距。如果设置为False,则在计算中将不使用截距(即,数据应中心化)。 |
| normalize | bool, default=Falsefit_intercept设置为False 时,将忽略此参数。如果为True,则在回归之前通过减去均值并除以l2-范数来对回归变量X进行归一化。如果你希望标准化,请先使用 sklearn.preprocessing.StandardScaler,然后调用fit 估算器并设置normalize=False。 |
| copy_X | bool, default=True 如果为True,将复制X;否则X可能会被覆盖。 |
| n_jobs | int, default=None 用于计算的核心数。这只会为n_targets> 1和足够大的问题提供加速。 除非在上下文中设置了 joblib.parallel_backend参数,否则None表示1 。 -1表示使用所有处理器。更多详细信息,请参见词汇表。 |
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| coef_ | array of shape (n_features, ) or (n_targets, n_features) 线性回归问题的估计系数。如果在拟合过程中传递了多个目标(y 2D),则这是一个二维数组,形状为(n_targets, n_features),而如果仅传递了一个目标,则是长度为n_features的一维数组。 |
| rank_ | int 矩阵 X的秩。仅在X是密集矩阵时可用。 |
| singular_ | array of shape (min(X, y),)X的奇异值。仅在X是密集矩阵时可用。 |
| intercept_ | float or array of shape (n_targets,) 线性模型中的截距项。如果设置 fit_intercept = False,则截距为0.0 。 |
另见
Ridge回归通过使用L2正则化对系数的大小进行惩罚来解决普通最小二乘的一些问题。
Lasso是一个线性模型,它使用L1正则化来估计稀疏系数。
sklearn.linear_model.ElasticNetElastic-Net是使用系数的L1和L2-范数正则化训练的线性回归模型。
注
从实现的角度来看,这只是包装为预测对象的普通最小二乘(scipy.linalg.lstsq)。
示例
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
>>> X = np.array([[1, 1], [1, 2], [2, 2], [2, 3]])
>>> # y = 1 * x_0 + 2 * x_1 + 3
>>> y = np.dot(X, np.array([1, 2])) + 3
>>> reg = LinearRegression().fit(X, y)
>>> reg.score(X, y)
1.0
>>> reg.coef_
array([1., 2.])
>>> reg.intercept_
3.0000...
>>> reg.predict(np.array([[3, 5]]))
array([16.])
方法
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
fit(self, X, y[, sample_weight]) |
拟合线性模型。 |
get_params(self[, deep]) |
获取此估计器的参数。 |
predict(self, X) |
使用线性模型进行预测。 |
score(self, X, y[, sample_weight]) |
返回预测的确定系数R ^ 2。 |
set_params(self, **params) |
设置此估计器的参数。 |
__init__(self, *, fit_intercept=True, normalize=False, copy_X=True, n_jobs=None)
初始化self, 请参阅help(type(self))以获得准确的说明。
fit(self,X,y,sample_weight = None )
[源码]
拟合线性模型。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | {ndarray, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features) 训练数据 |
| y | array-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_targets) 目标标签。如有必要,将强制转换为X的类型。 |
| sample_weight | array-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None 每个样本的权重 *0.17版中的新功能:sample_weight参数支持LinearRegression。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| self | returns an instance of self. 返回估计器的实例。 |
get_params(self,deep = True )
[源码]
获取此估计器的参数。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| deep | bool, default=True 如果为True,返回此估计器和所包含子对象的参数。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| params | mapping of string to any 参数名称映射到其值。 |
predict(self, X)
[源码]
使用线性模型进行预测。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | array_like or sparse matrix, shape (n_samples, n_features) 样本数据 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| C | array, shape [n_samples] 返回预测值。 |
score(self,X,y,sample_weight = None )
[源码]
返回预测的确定系数R ^ 2。
系数R ^ 2定义为(1- u / v),其中u是残差平方和((y_true-y_pred)** 2).sum(),而v是总平方和((y_true- y_true.mean())** 2).sum()。可能的最高得分为1.0,并且也可能为负(因为该模型可能会更差)。一个常数模型总是预测y的期望值,而不考虑输入特征,得到的R^2得分为0.0。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | array-like of shape (n_samples, n_features) 测试样本。对于某些估计量,这可以是预先计算的内核矩阵或通用对象列表,形状为(n_samples,n_samples_fitted),其中n_samples_fitted是用于拟合估计器的样本数。 |
| y | array-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs) X的真实值。 |
| sample_weight | array-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None 样本权重。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| score | float 预测值与真实值的R^2。 |
注
调用回归器中的score时使用的R2分数,multioutput='uniform_average'从0.23版开始使用 ,与r2_score默认值保持一致。这会影响多输出回归的score方法( MultiOutputRegressor除外)。
set_params(self, **params)
[源码]
设置此估算器的参数。
该方法适用于简单的估计器以及嵌套对象(例如管道)。后者具有形式为 <component>__<parameter>的参数,这样就可以更新嵌套对象的每个组件。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| **params | dict 估计器参数。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| self | object 估计器实例。 |