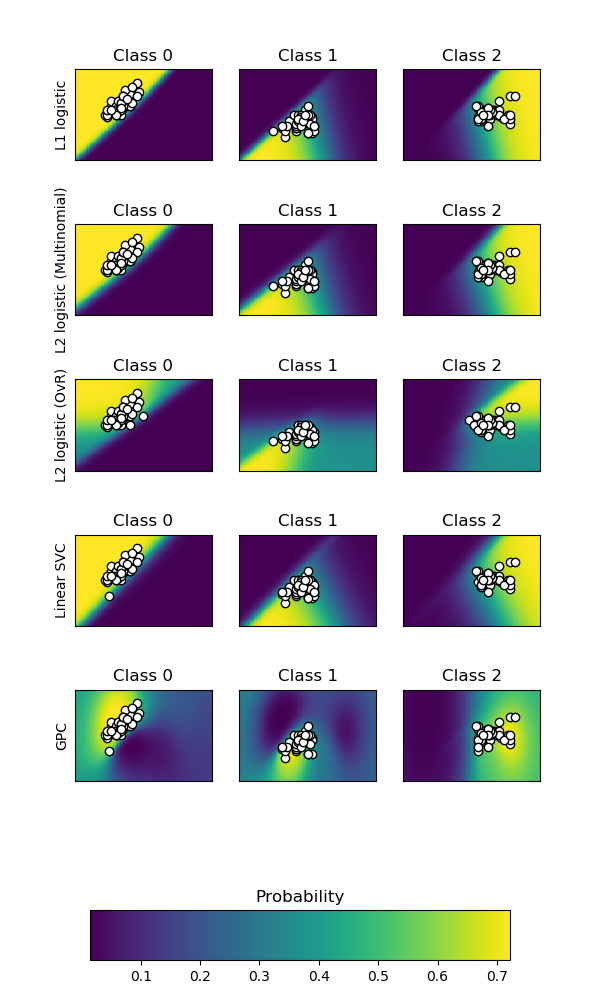
sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression¶
class sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression(penalty='l2', *, dual=False, tol=0.0001, C=1.0, fit_intercept=True, intercept_scaling=1, class_weight=None, random_state=None, solver='lbfgs', max_iter=100, multi_class='auto', verbose=0, warm_start=False, n_jobs=None, l1_ratio=None)
Logistic回归(又名logit,MaxEnt)分类器。
在多类情况下,如果将“ multi_class”选项设置为“ ovr”,则训练算法将使用“一对剩余”(OvR)方案;如果将“ multi_class”选项设置为“multinomial(多项式)”,则使用交叉熵损失。(当前,只有“ lbfgs”,“ sag”,“ saga”和“ newton-cg”求解器支持“多项式”选项。)
此类使用'liblinear'库,'newton-cg','sag','saga'和'lbfgs'求解器实现正则逻辑回归。请注意,默认情况下将应用正则化。它可以处理密集和稀疏输入。使用C排序数组或包含64位浮点数的CSR矩阵可获得最佳性能;其他任何输入格式将被转换(并复制)。
“ newton-cg”,“ sag”和“ lbfgs”求解器支持带有原始公式的L2正则化或不应用正则化。“ liblinear”求解器支持L1和L2正则化,仅针对L2罚分采用双重公式。只有“ saga”求解器支持Elastic-Net正则化。
在用户指南中阅读更多内容。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| penalty | {‘L1’, ‘L2’, ‘elasticnet’, ‘none’}, default=’L2’ 用于指定处罚中使用的规范。'newton-cg','sag'和'lbfgs'求解器仅支持L2惩罚。仅“ saga”求解器支持“ elasticnet”。如果为“ none”(liblinear求解器不支持),则不应用任何正则化。 版本0.19中的新功能: SAGA求解器的惩罚为L1(允许“multinomial” + L1) |
| dual | bool, default=False 是否对偶化。仅对liblinear求解器使用L2惩罚时进行对偶化。当n_samples> n_features时,首选dual = False。 |
| tol | float, default=1e-4 停止的容差标准。 |
| C | float, default=1.0 正则强度的倒数;必须为正浮点数。与支持向量机一样,较小的值指定更强的正则化。 |
| fit_intercept | bool, default=True 是否将常量(aka偏置或截距)添加到决策函数。 |
| intercept_scaling | float, default=1 仅在使用求解器“ liblinear”并将self.fit_intercept设置为True时有用。在这种情况下,x变为[x,self.intercept_scaling],即将常量值等于intercept_scaling的“合成”特征附加到实例矢量。截距变为 intercept_scaling * synthetic_feature_weight注意!与所有其他特征一样,合成特征权重也要经过L1 / L2正则化。为了减轻正则化对合成特征权重(以及因此对截距)的影响,必须增加intercept_scaling。 |
| class_weight | dict or ‘balanced’, default=None 以 {class_label: weight}的形式与类别关联的权重。如果没有给出,所有类别的权重都应该是1。“balanced”模式使用y的值来自动调整为与输入数据中的类频率成反比的权重。如 n_samples / (n_classes * np.bincount(y))请注意,如果指定了sample_weight,则这些权重将与sample_weight(通过fit方法传递)相乘 *0.17版中的新功能:*class_weight ='balanced' |
| random_state | int, RandomState instance, default=None 在 solver=='sag','saga'或'liblinear'时,用于随机整理数据。有关详细信息,请参见词汇表。 |
| solver | {‘newton-cg’, ‘lbfgs’, ‘liblinear’, ‘sag’, ‘saga’}, default=’lbfgs’ 用于优化问题的算法。 - 对于小型数据集,“ liblinear”是一个不错的选择,而对于大型数据集,“ sag”和“ saga”更快。 - 对于多类分类问题,只有'newton-cg' ,'sag','saga' 和 'lbfgs' 处理多项式损失。“ liblinear”仅限于“一站式”计划。 - 'newton-cg','lbfgs','sag'和'saga'处理L2或不惩罚 - 'liblinear'和'saga'也可以处理L1罚款 - “ saga”还支持“ elasticnet”惩罚 - 'liblinear'不支持设置 penalty='none'请注意,只有在比例大致相同的要素上才能保证“ sag”和“ saga”快速收敛。您可以使用sklearn.preprocessing中的缩放器对数据进行预处理。 *版本0.17中的新功能:*随机平均梯度下降求解器。 0.19版中的新功能: SAGA求解器。 在版本0.22中更改:默认求解器在0.22中从“ liblinear”更改为“ lbfgs”。 |
| max_iter | int, default=100 求解程序收敛的最大迭代次数。 |
| multi_class | {‘auto’, ‘ovr’, ‘multinomial’}, default=’auto’ 如果选择的选项是“ ovr”,则每个标签都看做二分类问题。对于“multinomial”,即使数据是二分类的,损失最小是多项式损失拟合整个概率分布。当solver ='liblinear' 时, 'multinomial' 不可用。如果数据是二分类的,或者如果Solver ='liblinear',则'auto'选择'ovr',否则选择'multinomial'。 *版本0.18中的新功能:*用于“多项式”情况的随机平均梯度下降求解器。 *在版本0.22中更改:在版本0.22中,*默认值从'ovr'更改为'auto'。 |
| verbose | int, default=0 对于liblinear和lbfgs求解器,将verbose设置为任何正数以表示输出日志的详细程度。 |
| warm_start | bool, default=False 设置为True时,重用前面调用的解决方案来进行初始化,否则,只清除前面的解决方案。这个参数对于线性求解器无用。请参阅词汇表。 0.17版中的新功能:**warm_start支持lbfgs,newton-cg,sag和saga求解器。 |
| n_jobs | int, default=None 当multi_class ='ovr'”,在对类进行并行化时使用的CPU内核数。将 solver设置为“ liblinear”时,无论是否指定“ multi_class” ,都将忽略此参数。除非设置了joblib.parallel_backend 参数,否则None表示1 。 -1表示使用所有处理器。有关更多详细信息,请参见词汇表。 |
| l1_ratio | float, default=None Elastic-Net混合参数,取值范围 0 <= l1_ratio <= 1。仅在penalty='elasticnet'时使用。设置l1_ratio=0等同于使用penalty='l2',而设置l1_ratio=1等同于使用penalty='l1'。对于0 < l1_ratio <1,惩罚是L1和L2的组合。 |
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| classes_ | ndarray of shape (n_classes, ) 分类器已知的类别标签列表。 |
| coef_ | ndarray of shape (1, n_features) or (n_classes, n_features) 决策函数中特征的系数。 coef_当给定问题为二分类时,其形状为(1,n_features)。特别地,当时multi_class='multinomial',coef_对应于输出1(真),并且-coef_对应于输出0(假)。 |
| intercept_ | ndarray of shape (1,) or (n_classes,) 添加到决策函数的截距(也称为偏差)。 如果 fit_intercept设置为False,则截距设置为零。 intercept_当给定问题为二分类时,其形状为(1,)。特别地,当multi_class='multinomial'时,intercept_ 对应于结果1(真),并且-intercept_对应于结果0(假)。 |
| n_iter_ | ndarray of shape (n_classes,) or (1, ) 所有类的实际迭代数。如果是二分类或多项式,则仅返回1个元素。对于liblinear求解器,仅给出所有类的最大迭代次数。 *在0.20版中更改:*在SciPy <= 1.0.0中,lbfgs迭代次数可能超过 max_iter。n_iter_现在输出最大的max_iter。 |
另见
逐步训练的逻辑回归(当指定参数时
loss="log")。具有内置交叉验证的逻辑回归。
注
底层的C实现使用一个随机数生成器来选择适合模型的特性。因此,对于相同的输入数据,结果略有不同的情况并不少见。如果出现这种情况,尝试使用较小的tol参数。
在某些情况下,预测输出可能与独立liblinear的输出不匹配。请参见叙述文档中与liblinear的区别。
参考
L-BFGS-B – Software for Large-scale Bound-constrained Optimization
Ciyou Zhu, Richard Byrd, Jorge Nocedal and Jose Luis Morales. http://users.iems.northwestern.edu/~nocedal/lbfgsb.html
LIBLINEAR – A Library for Large Linear Classification
https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/liblinear/
SAG – Mark Schmidt, Nicolas Le Roux, and Francis Bach
Minimizing Finite Sums with the Stochastic Average Gradient https://hal.inria.fr/hal-00860051/document
SAGA – Defazio, A., Bach F. & Lacoste-Julien S. (2014).
SAGA: A Fast Incremental Gradient Method With Support for Non-Strongly Convex Composite Objectives https://arxiv.org/abs/1407.0202
Hsiang-Fu Yu, Fang-Lan Huang, Chih-Jen Lin (2011). Dual coordinate descent
methods for logistic regression and maximum entropy models. Machine Learning 85(1-2):41-75. https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/papers/maxent_dual.pdf
示例
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
>>> from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
>>> X, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True)
>>> clf = LogisticRegression(random_state=0).fit(X, y)
>>> clf.predict(X[:2, :])
array([0, 0])
>>> clf.predict_proba(X[:2, :])
array([[9.8...e-01, 1.8...e-02, 1.4...e-08],
[9.7...e-01, 2.8...e-02, ...e-08]])
>>> clf.score(X, y)
0.97...
方法
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
decision_function(self, X) |
预测样本的置信度得分。 |
densify(self) |
将系数矩阵转换为密集数组格式。 |
fit(self, X, y[, sample_weight]) |
根据给定的训练数据拟合模型。 |
get_params(self[, deep]) |
获取此估计器的参数。 |
predict(self, X) |
预测X中样本的类别标签。 |
predict_log_proba(self, X) |
预测概率估计的对数。 |
predict_proba(self, X) |
概率估计。 |
score(self, X, y[, sample_weight]) |
返回给定测试数据和标签上的平均准确度。 |
set_params(self, **params) |
设置此估计器的参数。 |
sparsify(self) |
将系数矩阵转换为稀疏格式。 |
__init__(self, penalty='l2', *, dual=False, tol=0.0001, C=1.0, fit_intercept=True, intercept_scaling=1, class_weight=None, random_state=None, solver='lbfgs', max_iter=100, multi_class='auto', verbose=0, warm_start=False, n_jobs=None, l1_ratio=None)
初始化self, 请参阅help(type(self))以获得准确的说明。
decision_function(self, X)
预测样本的置信度得分。
样本的置信度分数是该样本到超平面的符号距离。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | array_like or sparse matrix, shape (n_samples, n_features) 样本。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| array, shape=(n_samples,) if n_classes == 2 else (n_samples, n_classes) 每个(样本,类别)组合的置信度得分。在二分类情况下,self.classes_ [1]的置信度得分> 0表示将预测该类。 |
densify(self)
将系数矩阵转换为密集数组格式。
将coef_数值(返回)转换为numpy.ndarray。这是coef_的默认格式,并且是拟合模型所需的格式,因此仅在之前被稀疏化的模型上才需要调用此方法。否则,它是无操作的。
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| self | 拟合估计器。 |
fit(self,X,y,sample_weight = None )
根据给定的训练数据拟合模型。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | {array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features) 训练数据,其中n_samples是样本数,n_features是特征数。 |
| y | array-like of shape (n_samples,) 对应于X的目标向量。 |
| sample_weight | array-like of shape (n_samples,) default=None 分配给各个样本的权重数组。如果未设置,则为每个样本的权重都为1。 0.17版中的新功能:sample_weight支持LogisticRegression。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| self | 拟合估计器。 |
注
SAGA求解器支持float64和float32位数组。
get_params(self,deep = True )
获取此估计器的参数。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| deep | bool, default=True 如果为True,返回此估计器和所包含子对象的参数。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| params | mapping of string to any 参数名称映射到其值。 |
predict(self, X)
预测X中样本的类别标签。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | array_like or sparse matrix, shape (n_samples, n_features) 样本数据 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| C | array, shape [n_samples] 每个样本的预测类别标签。 |
predict_log_proba(self, X)
预测概率估计的对数。
返回按类别标签排序的所有类别的估计值。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | array-like of shape (n_samples, n_features) 要预测的数据,其中 n_samples是样本数, n_features是特征数。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| T | array-like of shape (n_samples, n_classes) 返回模型中每个类别的样本的对数概率,按 self.classes_中类别的顺序排序。 |
predict_proba(self, X)
概率估计。
返回按类别标签排序的所有类别的估计值。
对于multi_class问题,如果将multi_class设置为“multinomial”,则使用softmax函数查找每个类别的预测概率。否则使用one vs-rest方法,即使用logistic函数计算每个类别为正的概率。并在所有类别中标准化这些值。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | array-like of shape (n_samples, n_features) 要预测的数据,其中 n_samples是样本数, n_features是特征数。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| T | array-like of shape (n_samples, n_classes) 返回模型中每个类别的样本概率,类按 self.classes_中的顺序排序。 |
score(self, X, y, sample_weight=None)
返回给定测试数据和标签上的平均准确度。
在多标签分类中,这是子集准确性,这是一个严格的指标,因为你需要为每个样本正确预测标签集。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | array-like of shape (n_samples, n_features) 测试样本。 |
| y | array-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs) X的真实标签。 |
| sample_weight | array-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None 样本权重。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| score | float 预测标签与真实标签的平均准确度 |
set_params(self, **params)
设置此估算器的参数。
该方法适用于简单的估计器以及嵌套对象(例如管道)。后者具有形式参数 <component>__<parameter>,以便可以更新嵌套对象的每个组件。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| **params | dict 估计器参数。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| self | object 估计器实例。 |
sparsify(self)
将系数矩阵转换为稀疏格式。
将coef_数值转换为scipy.sparse矩阵,对于L1正规化的模型,该矩阵比通常的numpy.ndarray具有更高的内存和存储效率。
该intercept_数值未转换。
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| self | 拟合估计器。 |
注
对于非稀疏模型,即当coef_中零的个数不多时,这实际上可能会增加内存使用量,因此请谨慎使用此方法。经验法则是,可以使用(coef_ == 0).sum()计算得到的零元素的数量必须大于50%,这时的效果是显着的。
在调用densify之前,调用此方法将无法进一步使用partial_fit方法(如果有)。