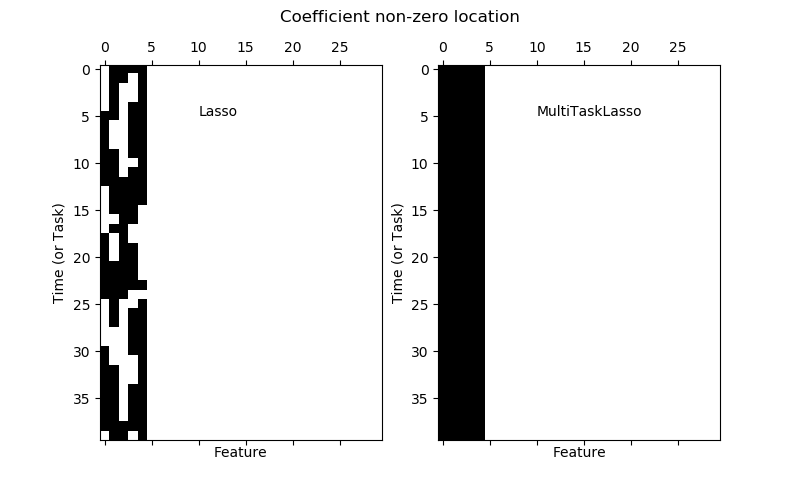
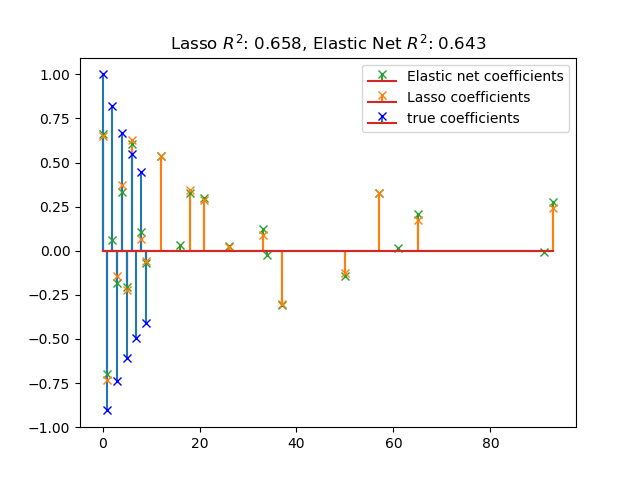
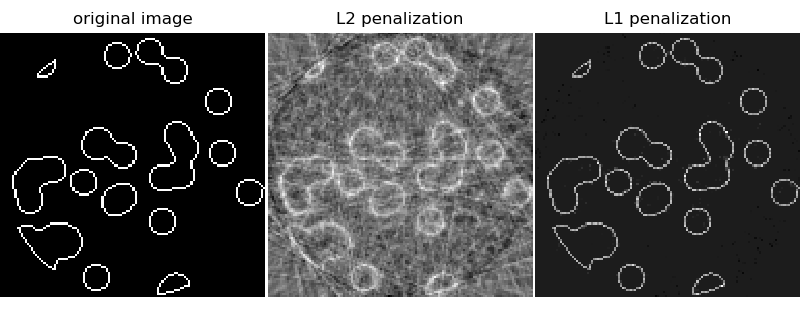
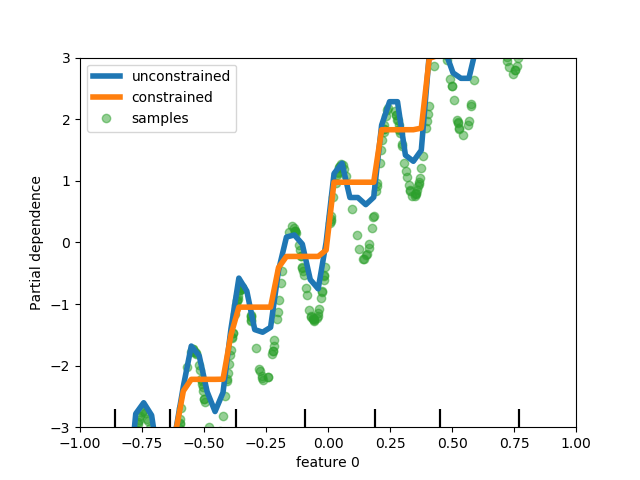
sklearn.linear_model.Lasso¶
class sklearn.linear_model.Lasso(alpha=1.0, *, fit_intercept=True, normalize=False, precompute=False, copy_X=True, max_iter=1000, tol=0.0001, warm_start=False, positive=False, random_state=None, selection='cyclic')
线性模型先经过L1训练作为正则化器(又称为Lasso)
Lasso的优化目标是:
从技术上讲,Lasso模型与l1_ratio=1.0(没有L2惩罚)时的弹性网有相同的目标函数。
在用户指南中阅读更多内容。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| alpha | float, default=1.0 乘以惩罚项的常数。默认为1.0。有关此参数的确切数学含义,请参见注释。 alpha = 0等同于由LinearRegression对象求解的普通最小二乘。由于数字原因,不建议alpha = 0与Lasso对象一起使用。鉴于此,你应该使用LinearRegression对象。 |
| fit_intercept | bool, default=True 是否估计截距。如果为 False,则假定数据已经中心化。 |
| normalize | bool, default=Falsefit_intercept设置为False 时,将忽略此参数。如果为True,则在回归之前通过减去均值并除以l2-范数来对回归变量X进行归一化。如果你希望标准化,请先使用 sklearn.preprocessing.StandardScaler,然后调用fit 估算器并设置normalize=False。 |
| precompute | bool or array-like of shape (n_features, n_features), default=False 是否使用预先计算的Gram矩阵来加快计算速度。Gram矩阵也可以作为参数传递。对于稀疏输入,此选项始终是 True以保持稀疏性。 |
| copy_X | default=True 如果 True,将复制X;否则X可能会被覆盖。 |
| max_iter | int, default=1000 最大迭代次数。 |
| tol | float, default=1e-4 优化的容忍度:如果更新小于 tol,优化代码将检查对偶间隙的最优性,并一直持续到它小于tol为止。 |
| warm_start | bool, default=False 设置为True时,重用前面调用的解决方案来进行初始化,否则,只清除前面的解决方案。请参阅词汇表。 |
| positive | bool, default=False 设置为 True时,强制系数为正。 |
| random_state | int, RandomState instance, default=None 更新特征随机选择的伪随机数生成器种子。在 selection=='random'时使用。在多个函数调用之间传递同一个整数实现可重复的输出。请参阅词汇表。 |
| selection | {‘cyclic’, ‘random’}, default=’cyclic’ 如果设置为“random”,则随机系数将在每次迭代时更新,而不是默认情况下按顺序遍历特征。这(设置为“random”)通常会导致收敛更快,尤其是当tol高于1e-4时。 |
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| coef_ | ndarray of shape (n_features,) or (n_targets, n_features) 参数向量(目标函数公式中的w) |
sparse_coef_ |
sparse matrix of shape (n_features, 1) or (n_targets, n_features) 拟合 coef_的稀疏表示 |
| intercept_ | float or ndarray of shape (n_targets,) 目标函数中的截距。 |
| n_iter_ | int or list of int 坐标下降求解器运行达到指定容忍度的迭代次数。 |
另见
用坐标下降法拟合模型。
为了避免不必要的内存重复,fit方法的X参数应该作为一个Fortran-contiguous numpy数组直接传递。
示例
>>> from sklearn import linear_model
>>> clf = linear_model.Lasso(alpha=0.1)
>>> clf.fit([[0,0], [1, 1], [2, 2]], [0, 1, 2])
Lasso(alpha=0.1)
>>> print(clf.coef_)
[0.85 0. ]
>>> print(clf.intercept_)
0.15...
方法
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
fit(X, y[, sample_weight, check_input]) |
用坐标下降法拟合模型。 |
get_params([deep]) |
获取此估计器的参数。 |
path(X, y, *[, l1_ratio, eps, n_alphas, …]) |
计算具有坐标下降的弹性网路径。 |
predict(X) |
使用线性模型进行预测。 |
score(X, y[, sample_weight]) |
返回预测的确定系数R ^ 2。 |
set_params(**params) |
设置此估算器的参数。 |
__init__(alpha=1.0, *, fit_intercept=True, normalize=False, precompute=False, copy_X=True, max_iter=1000, tol=0.0001, warm_start=False, positive=False, random_state=None, selection='cyclic')
初始化self, 请参阅help(type(self))以获得准确的说明。
fit(X, y, sample_weight=None, check_input=True)
用坐标下降法拟合模型。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | {ndarray, sparse matrix} of (n_samples, n_features) 样本数据。 |
| y | {ndarray, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_targets) 目标值。如有必要,将强制转换为X的数据类型 |
| sample_weight | float or array-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None 样本权重。 |
| check_input | bool, default=True 允许绕过多个输入检查。除非你知道自己要做什么,否则不要使用此参数。 |
注
坐标下降法是一次考虑数据的每一列的算法,因此如有必要,它会自动将X输入转换为Fortran-contiguous的numpy数组。
为了避免内存重新分配,建议直接使用这种格式在内存中分配初始数据。
get_params(deep=True)
获取此估计量的参数。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| deep | bool, default=True 如果为True,则将返回此估算器和所包含子对象的参数。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| params | mapping of string to any 参数名称映射到其值。 |
static path(X, y, *, l1_ratio=0.5, eps=0.001, n_alphas=100, alphas=None, precompute='auto', Xy=None, copy_X=True, coef_init=None, verbose=False, return_n_iter=False, positive=False, check_input=True, **params)
计算具有坐标下降的弹性网路径。
弹性网优化函数针对单输出和多输出而变化。
对于单输出任务,它是:
对于多输出任务,它是:
这里
即每一行的范数之和。
在用户指南中阅读更多内容。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | {array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features) 训练数据。直接作为Fortran-contiguous数据传递,以避免不必要的内存重复。如果 y是单输出,则X 可以是稀疏的。 |
| y | {array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs) 目标值。 |
| l1_ratio | float, default=0.5 0到1之间的数字传递给弹性网(在L1和L2罚分之间缩放)。 l1_ratio=1对应于Lasso。 |
| eps | float, default=1e-3 路径的长度。 eps=1e-3意味着 alpha_min / alpha_max = 1e-3。 |
| n_alphas | int, default=100 沿着正则化路径的Alpha个数。 |
| alphas | ndarray, default=None 用于计算模型的alpha列表。如果为None,则自动设置Alpha。 |
| precompute | ‘auto’, bool or array-like of shape (n_features, n_features), default=’auto’ 是否使用预先计算的Gram矩阵来加快计算速度。Gram矩阵也可以作为参数传递。 |
| Xy | array-like of shape (n_features,) or (n_features, n_outputs), default=None Xy = np.dot(XT,y)可以预先计算。仅当预先计算了Gram矩阵时才有用。 |
| copy_X | bool, default=True 如果 True,将复制X;否则X可能会被覆盖。 |
| coef_init | ndarray of shape (n_features, ), default=None 系数的初始值。 |
| verbose | bool or int, default=False 详细程度。 |
| return_n_iter | bool, default=False 是否返回迭代次数。 |
| positive | bool, default=False 如果设置为True,则强制系数为正。(仅当 y.ndim == 1时允许)。 |
| check_input | bool, default=True 跳过输入验证检查,包括提供的Gram矩阵(假设提供),假设在check_input = False时由调用方处理。 |
| **params | kwargs 传递给坐标下降求解器的关键字参数。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| alphas | ndarray of shape (n_alphas,) 沿模型计算路径的Alpha值。 |
| coefs | ndarray of shape (n_features, n_alphas) or (n_outputs, n_features, n_alphas) 沿路径的系数。 |
| dual_gaps | ndarray of shape (n_alphas,) 每个alpha优化结束时的双重间隔。 |
| n_iters | list of int 坐标下降优化器为达到每个alpha的指定容差所进行的迭代次数。(当 return_n_iter设置为True 时返回)。 |
另见
注
有关示例,请参见 examples / linear_model / plot_lasso_coordinate_descent_path.py。
predict(X)
[源码]
使用线性模型进行预测。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | array_like or sparse matrix, shape (n_samples, n_features) 样本数据 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| C | array, shape (n_samples,) 返回预测值。 |
score(X, y, sample_weight=None)
[源码]
返回预测的确定系数R ^ 2。
系数R ^ 2定义为(1- u / v),其中u是残差平方和((y_true-y_pred)** 2).sum(),而v是总平方和((y_true- y_true.mean())** 2).sum()。可能的最高得分为1.0,并且也可能为负(因为该模型可能会更差)。一个常数模型总是预测y的期望值,而不考虑输入特征,得到的R^2得分为0.0。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | array-like of shape (n_samples, n_features) 测试样本。对于某些估计量,这可以是预先计算的内核矩阵或通用对象列表,形状为(n_samples,n_samples_fitted),其中n_samples_fitted是用于拟合估计器的样本数。 |
| y | array-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs) X的真实值。 |
| sample_weight | array-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None 样本权重。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| score | float 预测值与真实值的R^2。 |
注
调用回归器中的score时使用的R2分数,multioutput='uniform_average'从0.23版开始使用 ,与r2_score默认值保持一致。这会影响多输出回归的score方法( MultiOutputRegressor除外)。
set_params(**params)
[源码]
设置此估计器的参数。
该方法适用于简单的估计器以及嵌套对象(例如管道)。后者具有形式为 <component>__<parameter>的参数,这样就可以更新嵌套对象的每个组件。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| **params | dict 估计器参数。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| self | object 估计器实例。 |
property sparse_coef_
拟合coef_的稀疏表示