sklearn.ensemble.HistGradientBoostingRegressor¶
class sklearn.ensemble.HistGradientBoostingRegressor(loss='least_squares', *, learning_rate=0.1, max_iter=100, max_leaf_nodes=31, max_depth=None, min_samples_leaf=20, l2_regularization=0.0, max_bins=255, monotonic_cst=None, warm_start=False, early_stopping='auto', scoring='loss', validation_fraction=0.1, n_iter_no_change=10, tol=1e-07, verbose=0, random_state=None)
基于直方图的梯度提升回归树。
对于大数据集(n_samples >= 10,000),该估计器比梯度提升回归器GradientBoostingRegressor快得多。
这个估计器对缺失值(nan)有本地支持。在训练过程中,树种植根据潜在的增益,在每个分割点学习缺失值的样本是应该去左子节点还是去右子节点。在进行预测时,缺省值的样本将被分配到左子节点或右子节点。如果在训练过程中没有遇到给定特征的缺失值,那么缺失值的样本将被映射到拥有最多样本的子特征。
这个实现是受LightGBM的启发。
注意,这个估计器目前还处于测试阶段: 预测和API可能会在没有任何弃用周期的情况下发生变化。要使用它,您需要显式导入enable_hist_gradient_boosting:
>>> # explicitly require this experimental feature
>>> from sklearn.experimental import enable_hist_gradient_boosting # noqa
>>> # now you can import normally from ensemble
>>> from sklearn.ensemble import HistGradientBoostingClassifier
请参阅用户指南获取更多信息。
0.21版本新功能。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| loss | {‘least_squares’, ‘least_absolute_deviation’, ‘poisson’}, optional (default=’least_squares’) 在增压过程中使用的损失函数。请注意,“最小二乘”和“泊松”损失实际上实现了“一半最小二乘损失”和“一半泊松偏差”来简化梯度的计算。此外,“poisson”损失内部使用一个 log-link,并要求y >= 0 |
| learning_rate | float, optional (default=0.1) 学习率,也称为缩水率。这被用作叶值的一个乘法因子。使用 1表示不缩水。 |
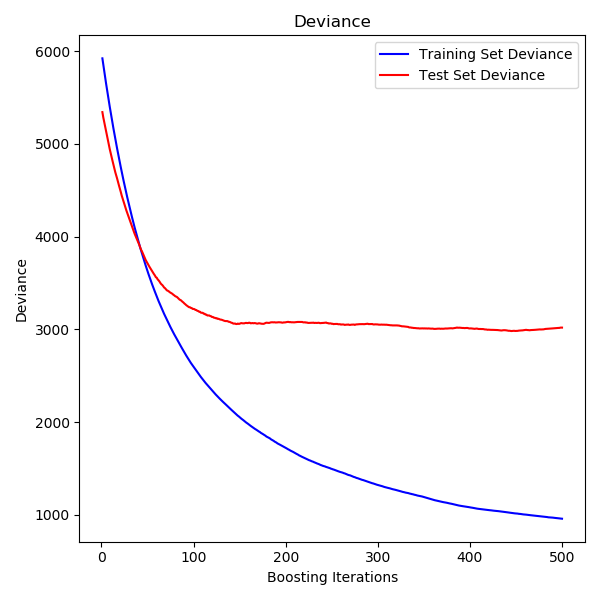
| max_iter | int, optional (default=100) 提升过程的最大迭代次数,即树的最大数量。 |
| max_leaf_nodes | int or None, optional (default=31) 每棵树的最大叶节点数。必须严格大于1。如果没有,就没有最大限制。 |
| max_depth | int or None, optional (default=None) 每棵树的最大深度。树的深度是指从根到最深叶子的边数。默认情况下深度没有限制。 |
| min_samples_leaf | int, optional (default=20) 每个叶子的最小样本数。对于少于几百个样本的小数据集,建议降低这个值,因为只会建立非常浅的树。 |
| l2_regularization | float, optional (default=0) L2正则化参数。使用0表示不正则化(默认)。 |
| max_bins | int, optional (default=255) 用于非缺失值的最大桶数。在训练之前,输入数组X的每个特征都被放入整数值的箱子中,这使得训练的速度更快。具有少量惟一值的特性可能使用小于 max_bins。除了max_bins外,还会为缺少的值保留一个容器。不能大于255。 |
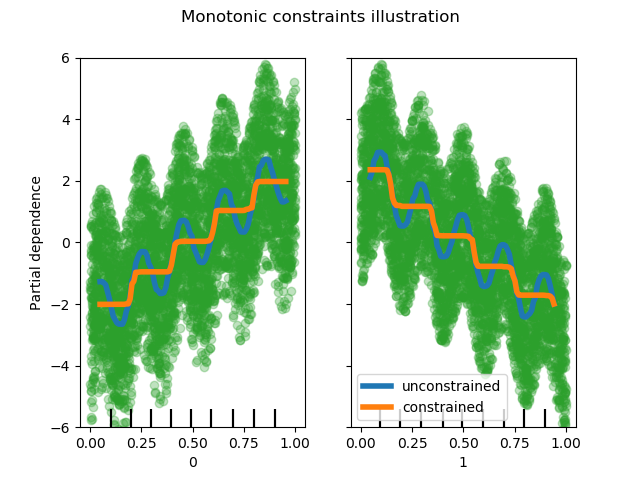
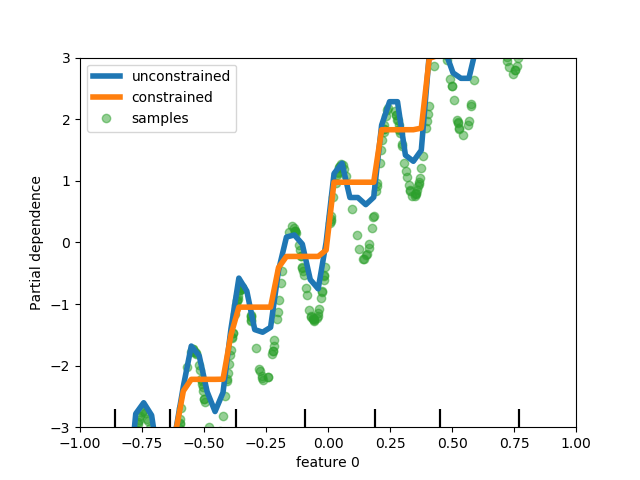
| monotonic_cst | array-like of int of shape (n_features), default=None 表示要对每个特征执行的单调约束。-1、1、0分别为正约束、负约束和无约束。请参阅用户指南获取更多信息。 |
| warm_start | bool, optional (default=False) 当设置为True时,重用前面调用的解决方案,以适应并向集成添加更多的评估器。为了使结果有效,估计器应该只在相同的数据上重新训练。详见 术语表。 |
| early_stopping | ‘auto’ or bool (default=’auto’) 如果使用“auto”,则在样本大小大于10000时启用早期停止。如果为True,则启用早期停止,否则禁用早期停止。 |
| scoring | str or callable or None, optional (default=’loss’) 用于早停的计分参数。它可以是单个字符串(参见The scoring parameter: defining model evaluation rules),也可以是可调用的(参见Defining your scoring strategy from metric functions)。如果没有,则使用估计器的默认得分器。如果计分=“损失”,则根据损失值检查提前停止。仅在提前停止时使用。 |
| validation_fraction | int or float or None, optional (default=0.1) 训练数据的比例(或绝对大小),预留为验证数据,以便早期停止。如果没有,则对训练数据进行早期停止。仅在提前停止时使用。 |
| n_iter_no_change | int, optional (default=10) 用来决定什么时候“早停止”。当最后的 n_iter_no_change得分在一定程度上都没有优于n_iter_no_change - 1的时候,拟合过程就会停止。仅在提前停止时使用。 |
| tol | float or None, optional (default=1e-7) 在比较早期停止期间的分数时使用的绝对容忍度。容忍度越高,我们越有可能提前停止:容忍度越高,意味着后续迭代将更难被认为是参考分数的改进。 |
| verbose | int, optional (default=0) 冗长的水平。如果不是零,打印一些关于拟合过程的信息。 |
| random_state | int, np.random.RandomStateInstance or None, optional (default=None) 伪随机数生成器,用于控制封装过程中的子采样,以及在启用早期停止时,列车/验证数据分离。在多个函数调用之间传递可重复输出的int。详见 术语表。 |
| 属性 | 参数 |
|---|---|
| n_iter_ | int 早期停止所选择的迭代次数,取决于 early_stop参数。否则它对应max_iter。 |
| n_trees_per_iteration_ | int 在每次迭代中构建的树的数量。对于回归项,这总是1。 |
| train_score_ | ndarray, shape (n_iter_+1,) 训练数据每次迭代时的得分。第一个条目是在第一次迭代之前集合的分数。根据评分参数计算分数。如果评分不是“损失”,则对最多10,000个样本的子集计算得分。空如果没有早期停止。 |
| validation_score_ | ndarray, shape (n_iter_+1,) 在每一次迭代中显示的验证数据的分数。第一个条目是在第一次迭代之前集合的分数。根据评分参数计算分数。如果没有早期停止,则为空;如果v alidation_fraction为None。 |
>>> # To use this experimental feature, we need to explicitly ask for it:
>>> from sklearn.experimental import enable_hist_gradient_boosting # noqa
>>> from sklearn.ensemble import HistGradientBoostingRegressor
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_diabetes
>>> X, y = load_diabetes(return_X_y=True)
>>> est = HistGradientBoostingRegressor().fit(X, y)
>>> est.score(X, y)
0.92...
方法
| 方法 | 参数 |
|---|---|
fit(X, y[, sample_weight]) |
拟合梯度助推模型。 |
get_params([deep]) |
获取这个估计器的参数。 |
predict(X) |
预测X的值。 |
score(X, y[, sample_weight]) |
返回预测的决定系数R^2。 |
set_params(**params) |
设置这个估计器的参数。 |
__init__(loss='least_squares', *, learning_rate=0.1, max_iter=100, max_leaf_nodes=31, max_depth=None, min_samples_leaf=20, l2_regularization=0.0, max_bins=255, monotonic_cst=None, warm_start=False, early_stopping='auto', scoring='loss', validation_fraction=0.1, n_iter_no_change=10, tol=1e-07, verbose=0, random_state=None)
初始化self。 使用help(type(self)) 获取准确的说明。
fit(X, y, sample_weight=None)
拟合梯度提升模型。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | array-like of shape (n_samples, n_features) 输入样本。 |
| y | array-like of shape (n_samples,) 目标值 |
| sample_weight | array-like of shape (n_samples,) default=None 权重和训练数据 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| self | object |
get_params(deep=True)
获取这个估计器的参数。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| deep | bool, default=True 如果为真,将返回此估计器的参数以及包含的作为估计器的子对象。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| params | mapping of string to any 参数名称映射到它们的值。 |
predict(X)
预测X的值。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | array-like, shape (n_samples, n_features) 输入样本 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| y | ndarray, shape (n_samples,) 预测值 |
score(X, y, sample_weight=None)
返回预测的决定系数R^2。
定义系数R^2为(1 - u/v),其中u为(y_true - y_pred) ** 2).sum()的残差平方和,v为(y_true - y_true.mean()) ** 2).sum()的平方和。最好的可能的分数是1.0,它可能是负的(因为模型可以任意地变糟)。一个常数模型总是预测y的期望值,不考虑输入特征,得到的R^2得分为0.0。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | array-like of shape (n_samples, n_features) 测试样品。对于某些估计器,这可能是一个预先计算的内核矩阵或一列通用对象,而不是形状= (n_samples, n_samples_fitting),其中n_samples_fitting是用于拟合估计器的样本数量。 |
| y | array-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs) X的值 |
| sample_weight | array-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None 样本权重 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| score | float R^2 of self.predict(X) wrt. y. |
注意:
调用回归变量上的score时使用的R2 score来自0.23版本的multioutput='uniform_average'来保持与r2_score的默认值一致。这影响了所有多输出回归的评分方法(除了 MultiOutputRegressor)。
set_params(**params)
设置估计器参数
该方法适用于简单估计量和嵌套对象(如pipline)。后者具有形式为<component>_<parameter>的参数,这样就让更新嵌套对象的每个组件成为了可能。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| **params | dict 估计器参数 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| self | object 估计器实例 |