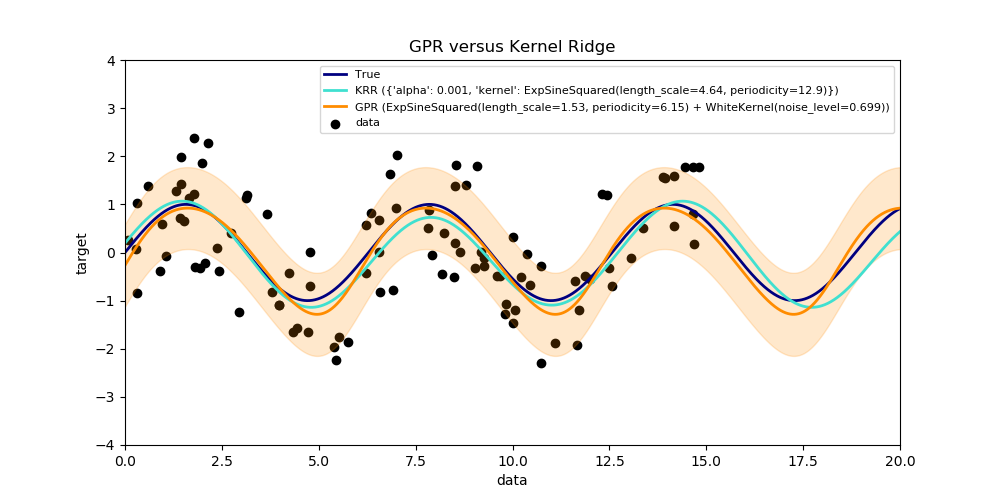
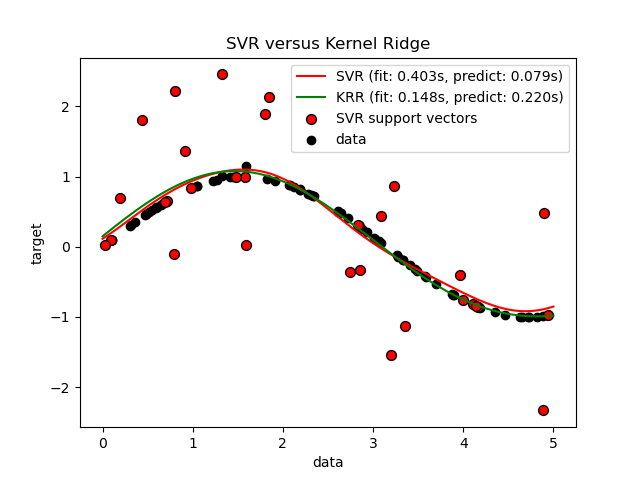
sklearn.kernel_ridge Kernel Ridge Regression¶
class sklearn.kernel_ridge.KernelRidge(alpha=1, *, kernel='linear', gamma=None, degree=3, coef0=1, kernel_params=None)
[源码]
内核岭回归。
内核岭回归(KRR)将岭回归(具有L2-范数正则化的线性最小二乘)与内核技巧结合在一起。因此,它学习了由各个内核和数据产生的空间中的线性函数。对于非线性内核,这对应于原始空间中的非线性函数。
KRR学习的模型的形式与支持向量回归(SVR)相同。但是,使用了不同的损失函数:KRR使用平方误差损失,而支持向量回归使用epsilon不敏感损失,两者均与L2正则化结合。与SVR相比,拟合KRR模型可以封闭形式进行,对于中等规模的数据集通常更快。另一方面,学习的模型是非稀疏的,因此比SVR慢,后者在预测时学习epsilon> 0的稀疏模型。
该估计器量有对多元回归的内置支持(即,当y是形状为[n_samples,n_targets]的二维数组时)。
在用户指南中阅读更多内容。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| alpha | float or array-like of shape (n_targets,) 正则强度;必须为正浮点数。正则化改善了问题的状况,并减少了估计的方差。较大的值表示更强的正则化。在其他线性模型中,Alpha对应于1/(2C),如logisticReturnation或sklearn.svm.LinearSVC.如果数组被传递,则假定惩罚是特定于目标的.因此它们必须在数量上对应。公式见Ridge regression and classification。 |
| kernel | string or callable, default=”linear” 内部使用的内核映射。此参数直接传递给 sklearn.metrics.pairwise.pairwise_kernel。如果kernel是字符串,则必须是pairwise.PAIRWISE_KERNEL_FUNCTIONS中的指标之一。如果kernel“预先计算”,则假定X为内核矩阵。另外,如果kernel是可调用函数,则在每对实例(行)上调用它,并记录结果值。可调用对象应将X的两行作为输入,并以单个数字返回相应的内核值。这意味着sklearn.metrics.pairwise不允许调用from ,因为它们在矩阵而不是单个样本上运行。请使用标识内核的字符串代替。 |
| gamma | float, default=None RBF,拉普拉斯算子,多项式,指数chi2和sigmoid kernels的Gamma参数。默认值的解释留给内核;请参阅sklearn.metrics.pairwise的文档。被其他内核忽略。 |
| degree | float, default=3 多项式内核的度。被其他内核忽略。 |
| coef0 | float, default=1 多项式和sigmoid kernels的系数为零。被其他内核忽略。 |
| kernel_params | mapping of string to any, optional 作为可调用对象传递的内核函数的其他参数(关键字参数)。 |
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| dual_coef_ | ndarray of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_targets) 核空间中权重向量的表示 |
| X_fit_ | {ndarray, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features) 训练数据,这也是预测所必需的。如果kernel ==“ precomputed”,则它是形状为(n_samples,n_samples)的预计算训练矩阵。 |
另见
线性岭回归。
支持使用libsvm实现的向量回归。
参考文献
1 Kevin P. Murphy “Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective”, The MIT Press chapter 14.4.3, pp. 492-493
实例
>>> from sklearn.kernel_ridge import KernelRidge
>>> import numpy as np
>>> n_samples, n_features = 10, 5
>>> rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
>>> y = rng.randn(n_samples)
>>> X = rng.randn(n_samples, n_features)
>>> clf = KernelRidge(alpha=1.0)
>>> clf.fit(X, y)
KernelRidge(alpha=1.0)
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
fit(self, X[, y, sample_weight]) |
拟合内核岭回归模型 |
get_params(self[, deep]) |
获取此估计量的参数。 |
predict(self, X) |
使用内核岭模型进行预测 |
score(self, X, y[, sample_weight]) |
返回预测的确定系数R ^ 2。 |
set_params(self, **params) |
设置此估算量的参数。 |
__init__(self, alpha=1, *, kernel='linear', gamma=None, degree=3, coef0=1, kernel_params=None)
[源码]
初始化self, 请参阅help(type(self))以获得准确的说明
fit(self, X, y=None, sample_weight=None)
[源码]
拟合内核岭回归模型
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | {array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features) 训练数据。如果kernel ==“ precomputed”,则它是形状为(n_samples,n_samples)的预计算内核矩阵。 |
| y | array-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_targets) 目标值 |
| sample_weight | float or array-like of shape [n_samples] 每个样本的单独权重,如果未通过则忽略。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| self | returns an instance of self. |
get_params(self, deep=True)
[源码]
获取此估计量的参数。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | {array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features) 如果为True,则将返回此估算量和作为估算量的所包含子对象的参数。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| C | ndarray of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_targets) 参数名称映射到其值。 |
score(self, X, y, sample_weight=None)
[源码]
返回预测的确定系数R ^ 2。
系数R^2定义为(1-u/v),其中u是平方的残差和((y_true-y_pred)2).sum(),v是平方和总和((y_true-y_true.means())2).sum()。最高得分可能为1.0,也可能为负(因为该模型可能会更差)。如果常量模型总是预测y的期望值,而不考虑输入特征,R^2则会得到分数0.0。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| X | array-like of shape (n_samples, n_features) 测试数据。对于某些估计量,可以是预先计算的内核矩阵或通用对象列表,而不是shape =(n_samples,n_samples_fitted),其中n_samples_fitted是用于估计量拟合的样本数。 |
| y | array-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs) X的真实值。 |
| sample_weight | array-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None 样本权重 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| score | float self.predict(X) wrt. y.的R^2 |
在回归函数上调用score时使用的R2 score使用0.23版本中的multioutput='uniform_average'来保持与R2\u score的默认值一致。这样处理会影响所有多输出回归函数的评分方法(MultiOutputRegressor除外)。
set_params(self, **params)
[源码]
设置此估算量的参数。
该方法适用于简单估计量以及嵌套对象(例如pipelines)。后者具有形式的参数。<component>__<parameter>这样就可以更新嵌套对象的每个组件。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| **params | dict 估算量参数。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| self | object 估计量实例。 |