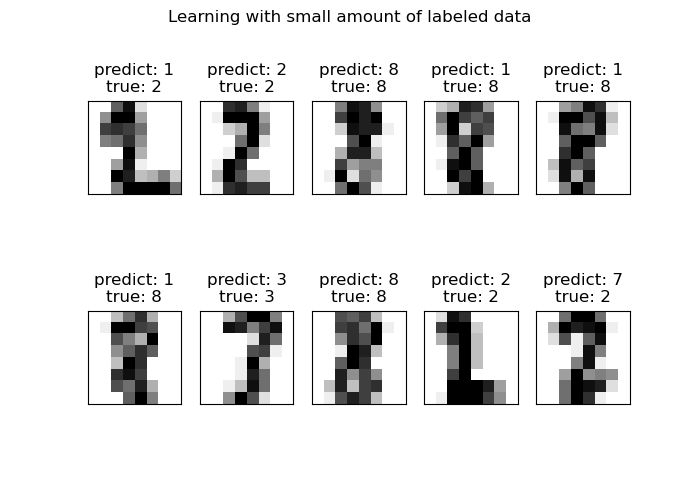
sklearn.metrics.confusion_matrix¶
sklearn.metrics.confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred, *, labels=None, sample_weight=None, normalize=None)
计算混淆矩阵以评估分类的准确性。
根据定义,混淆矩阵使得等于已知在第i组中并且预计在第j组中的观测次数。
因此,在二元分类中,真负例的计数为,假负例的计数为,真正例的计数为,假正例的计数为。
在用户指南中阅读更多内容。
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| y_true | array-like of shape (n_samples,) 真实目标值。 |
| y_pred | array-like of shape (n_samples,) 分类器返回的估计目标。 |
| labels | array-like of shape (n_classes), default=None 索引矩阵的标签列表。可用于重新排序或选择标签的子集。如果指定None,则那些在y_true或y_pred中至少出现一次的标签将按照排序使用。 |
| sample_weight | array-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None 样本权重。 版本0.18中的新功能。 |
| normalize | {‘true’, ‘pred’, ‘all’}, default=None 对真实(行),预测(列)条件或所有总体的混淆矩阵进行归一化。 如果为None,则不会对混淆矩阵进行归一化。 |
| 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| C | ndarray of shape (n_classes, n_classes) 混淆矩阵,其第i行和第j列条目指示真实标签为第i类且预测标签为第j类的样本数。 |
参考
1 Wikipedia entry for the Confusion matrix (Wikipedia and other references may use a different convention for axes)
示例
>>> from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
>>> y_true = [2, 0, 2, 2, 0, 1]
>>> y_pred = [0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 2]
>>> confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
array([[2, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 2]])
>>> y_true = ["cat", "ant", "cat", "cat", "ant", "bird"]
>>> y_pred = ["ant", "ant", "cat", "cat", "ant", "cat"]
>>> confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred, labels=["ant", "bird", "cat"])
array([[2, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 2]])
在二进制情况下,我们可以提取真实的正例,如下所示:
>>> tn, fp, fn, tp = confusion_matrix([0, 1, 0, 1], [1, 1, 1, 0]).ravel()
>>> (tn, fp, fn, tp)
(0, 2, 1, 1)