离散数据结构上的高斯过程¶
此示例说明如何使用高斯过程对非固定长度特征向量形式的数据进行回归和分类任务。这是通过核函数在离散结构(例如可变长度序列、树和图)直接操作实现的。
具体来说,这里的输入变量是一些以可变长度字符串形式存储的由字母‘A’、‘T’、‘C’和‘G’组成的基因序列,而在回归和分类任务中,输出变量分别是浮点数和真/假标签。
基因序列之间的核是用R-convolution[1]定义的,它是通过在一对字符串之间的所有字母对上集成一个二进制字母级核来定义的。
此示例将生成三个图。
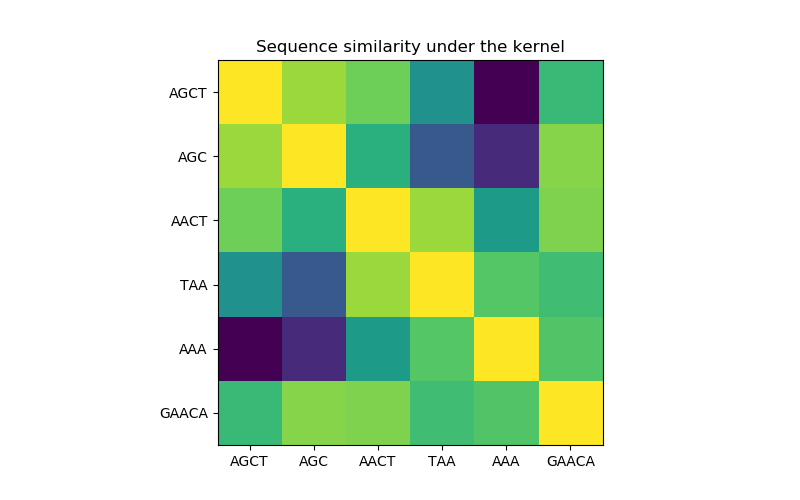
在第一个图中,我们使用颜色映射来可视化内核的值,即序列的相似性。这里较亮的颜色表示更高的相似性。
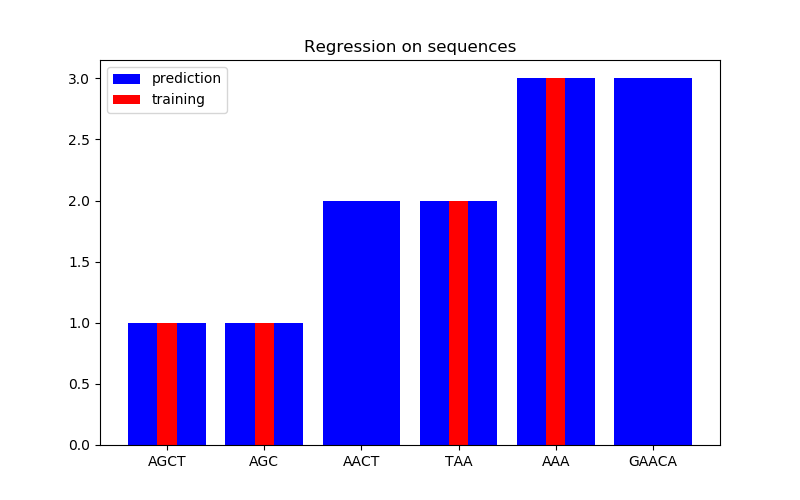
在第二个图中,我们在6个序列的数据集上给出了一些回归结果。这里我们使用第一、第二、第四和第五序列作为训练集,对第三和第六序列进行预测。
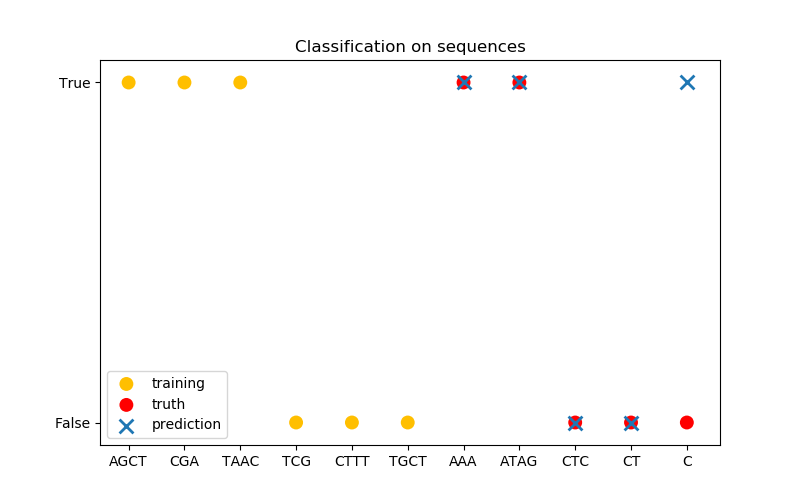
在第三张图中,我们通过对6序列进行训练来演示一个分类模型,并对另外5个序列进行预测。这里的基本事实是,序列中至少有一个‘A’。在这里,模型进行了四种正确的分类,其中一种分类失败。
1 Haussler, D. (1999). Convolution kernels on discrete structures (Vol. 646). Technical report, Department of Computer Science, University of California at Santa Cruz.
print(__doc__)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.gaussian_process.kernels import Kernel, Hyperparameter
from sklearn.gaussian_process.kernels import GenericKernelMixin
from sklearn.gaussian_process import GaussianProcessRegressor
from sklearn.gaussian_process import GaussianProcessClassifier
from sklearn.base import clone
class SequenceKernel(GenericKernelMixin, Kernel):
'''
A minimal (but valid) convolutional kernel for sequences of variable
lengths.'''
def __init__(self,
baseline_similarity=0.5,
baseline_similarity_bounds=(1e-5, 1)):
self.baseline_similarity = baseline_similarity
self.baseline_similarity_bounds = baseline_similarity_bounds
@property
def hyperparameter_baseline_similarity(self):
return Hyperparameter("baseline_similarity",
"numeric",
self.baseline_similarity_bounds)
def _f(self, s1, s2):
'''
kernel value between a pair of sequences
'''
return sum([1.0 if c1 == c2 else self.baseline_similarity
for c1 in s1
for c2 in s2])
def _g(self, s1, s2):
'''
kernel derivative between a pair of sequences
'''
return sum([0.0 if c1 == c2 else 1.0
for c1 in s1
for c2 in s2])
def __call__(self, X, Y=None, eval_gradient=False):
if Y is None:
Y = X
if eval_gradient:
return (np.array([[self._f(x, y) for y in Y] for x in X]),
np.array([[[self._g(x, y)] for y in Y] for x in X]))
else:
return np.array([[self._f(x, y) for y in Y] for x in X])
def diag(self, X):
return np.array([self._f(x, x) for x in X])
def is_stationary(self):
return False
def clone_with_theta(self, theta):
cloned = clone(self)
cloned.theta = theta
return cloned
kernel = SequenceKernel()
'''
Sequence similarity matrix under the kernel
===========================================
'''
X = np.array(['AGCT', 'AGC', 'AACT', 'TAA', 'AAA', 'GAACA'])
K = kernel(X)
D = kernel.diag(X)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
plt.imshow(np.diag(D**-0.5).dot(K).dot(np.diag(D**-0.5)))
plt.xticks(np.arange(len(X)), X)
plt.yticks(np.arange(len(X)), X)
plt.title('Sequence similarity under the kernel')
'''
Regression
==========
'''
X = np.array(['AGCT', 'AGC', 'AACT', 'TAA', 'AAA', 'GAACA'])
Y = np.array([1.0, 1.0, 2.0, 2.0, 3.0, 3.0])
training_idx = [0, 1, 3, 4]
gp = GaussianProcessRegressor(kernel=kernel)
gp.fit(X[training_idx], Y[training_idx])
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
plt.bar(np.arange(len(X)), gp.predict(X), color='b', label='prediction')
plt.bar(training_idx, Y[training_idx], width=0.2, color='r',
alpha=1, label='training')
plt.xticks(np.arange(len(X)), X)
plt.title('Regression on sequences')
plt.legend()
'''
Classification
==============
'''
X_train = np.array(['AGCT', 'CGA', 'TAAC', 'TCG', 'CTTT', 'TGCT'])
# whether there are 'A's in the sequence
Y_train = np.array([True, True, True, False, False, False])
gp = GaussianProcessClassifier(kernel)
gp.fit(X_train, Y_train)
X_test = ['AAA', 'ATAG', 'CTC', 'CT', 'C']
Y_test = [True, True, False, False, False]
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
plt.scatter(np.arange(len(X_train)), [1.0 if c else -1.0 for c in Y_train],
s=100, marker='o', edgecolor='none', facecolor=(1, 0.75, 0),
label='training')
plt.scatter(len(X_train) + np.arange(len(X_test)),
[1.0 if c else -1.0 for c in Y_test],
s=100, marker='o', edgecolor='none', facecolor='r', label='truth')
plt.scatter(len(X_train) + np.arange(len(X_test)),
[1.0 if c else -1.0 for c in gp.predict(X_test)],
s=100, marker='x', edgecolor=(0, 1.0, 0.3), linewidth=2,
label='prediction')
plt.xticks(np.arange(len(X_train) + len(X_test)),
np.concatenate((X_train, X_test)))
plt.yticks([-1, 1], [False, True])
plt.title('Classification on sequences')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
脚本的总运行时间:(0分0.260秒)
Download Python source code: plot_gpr_on_structured_data.py
Download Jupyter notebook: plot_gpr_on_structured_data.ipynb




