在iris数据集上的高斯过程分类¶
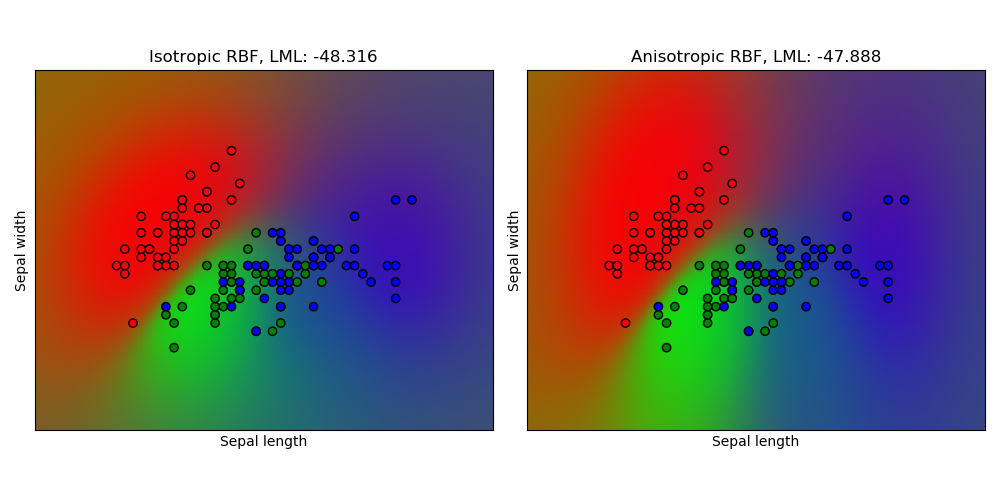
这个例子说明了在二维版本的iris数据集上,各向同性和各向异性径向基函数核(RBF)的GPC的预测概率。各向异性径向基函数核通过给两个特征维分配不同的长度尺度,得到略高的对数边际似然。
print(__doc__)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.gaussian_process import GaussianProcessClassifier
from sklearn.gaussian_process.kernels import RBF
# import some data to play with
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :2] # we only take the first two features.
y = np.array(iris.target, dtype=int)
h = .02 # step size in the mesh
kernel = 1.0 * RBF([1.0])
gpc_rbf_isotropic = GaussianProcessClassifier(kernel=kernel).fit(X, y)
kernel = 1.0 * RBF([1.0, 1.0])
gpc_rbf_anisotropic = GaussianProcessClassifier(kernel=kernel).fit(X, y)
# create a mesh to plot in
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
titles = ["Isotropic RBF", "Anisotropic RBF"]
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
for i, clf in enumerate((gpc_rbf_isotropic, gpc_rbf_anisotropic)):
# Plot the predicted probabilities. For that, we will assign a color to
# each point in the mesh [x_min, m_max]x[y_min, y_max].
plt.subplot(1, 2, i + 1)
Z = clf.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape((xx.shape[0], xx.shape[1], 3))
plt.imshow(Z, extent=(x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max), origin="lower")
# Plot also the training points
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=np.array(["r", "g", "b"])[y],
edgecolors=(0, 0, 0))
plt.xlabel('Sepal length')
plt.ylabel('Sepal width')
plt.xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
plt.ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.title("%s, LML: %.3f" %
(titles[i], clf.log_marginal_likelihood(clf.kernel_.theta)))
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
脚本的总运行时间:(0分3.967秒)




