GMM协方差¶
高斯混合模型几种协方差类型的证明。
有关估计器的更多信息,请参见高斯混合模型。
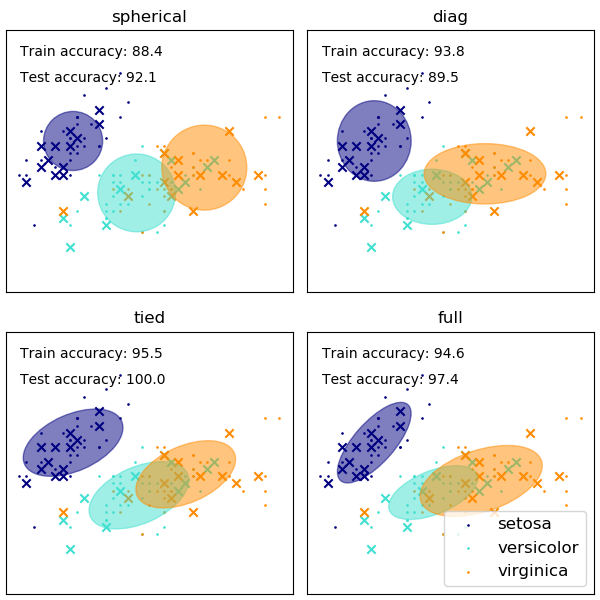
虽然GMM经常用于聚类,但我们可以将所获得的聚类与数据集中的实际类进行比较。我们用训练集中的类均值初始化高斯的均值,以使这种比较有效。
我们在iris数据集上使用多种GMM协方差类型, 并绘制了在训练集和测试集上的预测标签。我们比较了球形的、对角的、完全的、关联的协方差矩阵的GMM性能增加的顺序进行比较。虽然通常预计完全协方差表现最好,但在小数据集上往往会出现过拟合,并且不能很好地泛化到测试数据。在图中,训练数据显示为圆点,而测试数据显示为叉。iris数据集是四维的。这里只显示了前两个维度,因此一些点在其他维度中被分开。
# Author: Ron Weiss <ronweiss@gmail.com>, Gael Varoquaux
# Modified by Thierry Guillemot <thierry.guillemot.work@gmail.com>
# License: BSD 3 clause
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.mixture import GaussianMixture
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
print(__doc__)
colors = ['navy', 'turquoise', 'darkorange']
def make_ellipses(gmm, ax):
for n, color in enumerate(colors):
if gmm.covariance_type == 'full':
covariances = gmm.covariances_[n][:2, :2]
elif gmm.covariance_type == 'tied':
covariances = gmm.covariances_[:2, :2]
elif gmm.covariance_type == 'diag':
covariances = np.diag(gmm.covariances_[n][:2])
elif gmm.covariance_type == 'spherical':
covariances = np.eye(gmm.means_.shape[1]) * gmm.covariances_[n]
v, w = np.linalg.eigh(covariances)
u = w[0] / np.linalg.norm(w[0])
angle = np.arctan2(u[1], u[0])
angle = 180 * angle / np.pi # convert to degrees
v = 2. * np.sqrt(2.) * np.sqrt(v)
ell = mpl.patches.Ellipse(gmm.means_[n, :2], v[0], v[1],
180 + angle, color=color)
ell.set_clip_box(ax.bbox)
ell.set_alpha(0.5)
ax.add_artist(ell)
ax.set_aspect('equal', 'datalim')
iris = datasets.load_iris()
# Break up the dataset into non-overlapping training (75%) and testing
# (25%) sets.
skf = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=4)
# Only take the first fold.
train_index, test_index = next(iter(skf.split(iris.data, iris.target)))
X_train = iris.data[train_index]
y_train = iris.target[train_index]
X_test = iris.data[test_index]
y_test = iris.target[test_index]
n_classes = len(np.unique(y_train))
# Try GMMs using different types of covariances.
estimators = {cov_type: GaussianMixture(n_components=n_classes,
covariance_type=cov_type, max_iter=20, random_state=0)
for cov_type in ['spherical', 'diag', 'tied', 'full']}
n_estimators = len(estimators)
plt.figure(figsize=(3 * n_estimators // 2, 6))
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=.01, top=0.95, hspace=.15, wspace=.05,
left=.01, right=.99)
for index, (name, estimator) in enumerate(estimators.items()):
# Since we have class labels for the training data, we can
# initialize the GMM parameters in a supervised manner.
estimator.means_init = np.array([X_train[y_train == i].mean(axis=0)
for i in range(n_classes)])
# Train the other parameters using the EM algorithm.
estimator.fit(X_train)
h = plt.subplot(2, n_estimators // 2, index + 1)
make_ellipses(estimator, h)
for n, color in enumerate(colors):
data = iris.data[iris.target == n]
plt.scatter(data[:, 0], data[:, 1], s=0.8, color=color,
label=iris.target_names[n])
# Plot the test data with crosses
for n, color in enumerate(colors):
data = X_test[y_test == n]
plt.scatter(data[:, 0], data[:, 1], marker='x', color=color)
y_train_pred = estimator.predict(X_train)
train_accuracy = np.mean(y_train_pred.ravel() == y_train.ravel()) * 100
plt.text(0.05, 0.9, 'Train accuracy: %.1f' % train_accuracy,
transform=h.transAxes)
y_test_pred = estimator.predict(X_test)
test_accuracy = np.mean(y_test_pred.ravel() == y_test.ravel()) * 100
plt.text(0.05, 0.8, 'Test accuracy: %.1f' % test_accuracy,
transform=h.transAxes)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.title(name)
plt.legend(scatterpoints=1, loc='lower right', prop=dict(size=12))
plt.show()
脚本的总运行时间:(0分0.223秒)




