文本文档的核外分类¶
这是一个示例,展示了如何使用核外的方法来进行分类:从不适合主存的数据中学习。我们使用在线分类器,即支持partial_fit 方法,该分类器将提供大量的示例, 该方法别使用数据的一部分。为了保证特征空间随着时间的推移保持不变,我们利用HashingVectorizer将每个样本投影到相同的特征空间。这在文本分类中尤其有用,因为每批文本中都可能出现新的特征(单词)。
# Authors: Eustache Diemert <eustache@diemert.fr>
# @FedericoV <https://github.com/FedericoV/>
# License: BSD 3 clause
from glob import glob
import itertools
import os.path
import re
import tarfile
import time
import sys
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import rcParams
from html.parser import HTMLParser
from urllib.request import urlretrieve
from sklearn.datasets import get_data_home
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import HashingVectorizer
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
from sklearn.linear_model import PassiveAggressiveClassifier
from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
def _not_in_sphinx():
# Hack to detect whether we are running by the sphinx builder
return '__file__' in globals()
路透社数据集相关例程
本例中使用的数据集是UCI ML 存储库提供的Reuters-21578。它将在第一次运行时自动下载和解压缩。
class ReutersParser(HTMLParser):
"""Utility class to parse a SGML file and yield documents one at a time."""
def __init__(self, encoding='latin-1'):
HTMLParser.__init__(self)
self._reset()
self.encoding = encoding
def handle_starttag(self, tag, attrs):
method = 'start_' + tag
getattr(self, method, lambda x: None)(attrs)
def handle_endtag(self, tag):
method = 'end_' + tag
getattr(self, method, lambda: None)()
def _reset(self):
self.in_title = 0
self.in_body = 0
self.in_topics = 0
self.in_topic_d = 0
self.title = ""
self.body = ""
self.topics = []
self.topic_d = ""
def parse(self, fd):
self.docs = []
for chunk in fd:
self.feed(chunk.decode(self.encoding))
for doc in self.docs:
yield doc
self.docs = []
self.close()
def handle_data(self, data):
if self.in_body:
self.body += data
elif self.in_title:
self.title += data
elif self.in_topic_d:
self.topic_d += data
def start_reuters(self, attributes):
pass
def end_reuters(self):
self.body = re.sub(r'\s+', r' ', self.body)
self.docs.append({'title': self.title,
'body': self.body,
'topics': self.topics})
self._reset()
def start_title(self, attributes):
self.in_title = 1
def end_title(self):
self.in_title = 0
def start_body(self, attributes):
self.in_body = 1
def end_body(self):
self.in_body = 0
def start_topics(self, attributes):
self.in_topics = 1
def end_topics(self):
self.in_topics = 0
def start_d(self, attributes):
self.in_topic_d = 1
def end_d(self):
self.in_topic_d = 0
self.topics.append(self.topic_d)
self.topic_d = ""
def stream_reuters_documents(data_path=None):
"""Iterate over documents of the Reuters dataset.
The Reuters archive will automatically be downloaded and uncompressed if
the `data_path` directory does not exist.
Documents are represented as dictionaries with 'body' (str),
'title' (str), 'topics' (list(str)) keys.
"""
DOWNLOAD_URL = ('http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/'
'reuters21578-mld/reuters21578.tar.gz')
ARCHIVE_FILENAME = 'reuters21578.tar.gz'
if data_path is None:
data_path = os.path.join(get_data_home(), "reuters")
if not os.path.exists(data_path):
"""Download the dataset."""
print("downloading dataset (once and for all) into %s" %
data_path)
os.mkdir(data_path)
def progress(blocknum, bs, size):
total_sz_mb = '%.2f MB' % (size / 1e6)
current_sz_mb = '%.2f MB' % ((blocknum * bs) / 1e6)
if _not_in_sphinx():
sys.stdout.write(
'\rdownloaded %s / %s' % (current_sz_mb, total_sz_mb))
archive_path = os.path.join(data_path, ARCHIVE_FILENAME)
urlretrieve(DOWNLOAD_URL, filename=archive_path,
reporthook=progress)
if _not_in_sphinx():
sys.stdout.write('\r')
print("untarring Reuters dataset...")
tarfile.open(archive_path, 'r:gz').extractall(data_path)
print("done.")
parser = ReutersParser()
for filename in glob(os.path.join(data_path, "*.sgm")):
for doc in parser.parse(open(filename, 'rb')):
yield doc
main
创建矢量器,并将特征的数量限制在合理的最大值。
vectorizer = HashingVectorizer(decode_error='ignore', n_features=2 ** 18,
alternate_sign=False)
# Iterator over parsed Reuters SGML files.
data_stream = stream_reuters_documents()
# We learn a binary classification between the "acq" class and all the others.
# "acq" was chosen as it is more or less evenly distributed in the Reuters
# files. For other datasets, one should take care of creating a test set with
# a realistic portion of positive instances.
all_classes = np.array([0, 1])
positive_class = 'acq'
# Here are some classifiers that support the `partial_fit` method
partial_fit_classifiers = {
'SGD': SGDClassifier(max_iter=5),
'Perceptron': Perceptron(),
'NB Multinomial': MultinomialNB(alpha=0.01),
'Passive-Aggressive': PassiveAggressiveClassifier(),
}
def get_minibatch(doc_iter, size, pos_class=positive_class):
"""Extract a minibatch of examples, return a tuple X_text, y.
Note: size is before excluding invalid docs with no topics assigned.
"""
data = [('{title}\n\n{body}'.format(**doc), pos_class in doc['topics'])
for doc in itertools.islice(doc_iter, size)
if doc['topics']]
if not len(data):
return np.asarray([], dtype=int), np.asarray([], dtype=int)
X_text, y = zip(*data)
return X_text, np.asarray(y, dtype=int)
def iter_minibatches(doc_iter, minibatch_size):
"""Generator of minibatches."""
X_text, y = get_minibatch(doc_iter, minibatch_size)
while len(X_text):
yield X_text, y
X_text, y = get_minibatch(doc_iter, minibatch_size)
# test data statistics
test_stats = {'n_test': 0, 'n_test_pos': 0}
# First we hold out a number of examples to estimate accuracy
n_test_documents = 1000
tick = time.time()
X_test_text, y_test = get_minibatch(data_stream, 1000)
parsing_time = time.time() - tick
tick = time.time()
X_test = vectorizer.transform(X_test_text)
vectorizing_time = time.time() - tick
test_stats['n_test'] += len(y_test)
test_stats['n_test_pos'] += sum(y_test)
print("Test set is %d documents (%d positive)" % (len(y_test), sum(y_test)))
def progress(cls_name, stats):
"""Report progress information, return a string."""
duration = time.time() - stats['t0']
s = "%20s classifier : \t" % cls_name
s += "%(n_train)6d train docs (%(n_train_pos)6d positive) " % stats
s += "%(n_test)6d test docs (%(n_test_pos)6d positive) " % test_stats
s += "accuracy: %(accuracy).3f " % stats
s += "in %.2fs (%5d docs/s)" % (duration, stats['n_train'] / duration)
return s
cls_stats = {}
for cls_name in partial_fit_classifiers:
stats = {'n_train': 0, 'n_train_pos': 0,
'accuracy': 0.0, 'accuracy_history': [(0, 0)], 't0': time.time(),
'runtime_history': [(0, 0)], 'total_fit_time': 0.0}
cls_stats[cls_name] = stats
get_minibatch(data_stream, n_test_documents)
# Discard test set
# We will feed the classifier with mini-batches of 1000 documents; this means
# we have at most 1000 docs in memory at any time. The smaller the document
# batch, the bigger the relative overhead of the partial fit methods.
minibatch_size = 1000
# Create the data_stream that parses Reuters SGML files and iterates on
# documents as a stream.
minibatch_iterators = iter_minibatches(data_stream, minibatch_size)
total_vect_time = 0.0
# Main loop : iterate on mini-batches of examples
for i, (X_train_text, y_train) in enumerate(minibatch_iterators):
tick = time.time()
X_train = vectorizer.transform(X_train_text)
total_vect_time += time.time() - tick
for cls_name, cls in partial_fit_classifiers.items():
tick = time.time()
# update estimator with examples in the current mini-batch
cls.partial_fit(X_train, y_train, classes=all_classes)
# accumulate test accuracy stats
cls_stats[cls_name]['total_fit_time'] += time.time() - tick
cls_stats[cls_name]['n_train'] += X_train.shape[0]
cls_stats[cls_name]['n_train_pos'] += sum(y_train)
tick = time.time()
cls_stats[cls_name]['accuracy'] = cls.score(X_test, y_test)
cls_stats[cls_name]['prediction_time'] = time.time() - tick
acc_history = (cls_stats[cls_name]['accuracy'],
cls_stats[cls_name]['n_train'])
cls_stats[cls_name]['accuracy_history'].append(acc_history)
run_history = (cls_stats[cls_name]['accuracy'],
total_vect_time + cls_stats[cls_name]['total_fit_time'])
cls_stats[cls_name]['runtime_history'].append(run_history)
if i % 3 == 0:
print(progress(cls_name, cls_stats[cls_name]))
if i % 3 == 0:
print('\n')
downloading dataset (once and for all) into /home/circleci/scikit_learn_data/reuters
untarring Reuters dataset...
done.
Test set is 982 documents (90 positive)
SGD classifier : 966 train docs ( 88 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.923 in 0.93s ( 1038 docs/s)
Perceptron classifier : 966 train docs ( 88 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.929 in 0.93s ( 1033 docs/s)
NB Multinomial classifier : 966 train docs ( 88 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.909 in 0.97s ( 992 docs/s)
Passive-Aggressive classifier : 966 train docs ( 88 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.939 in 0.98s ( 987 docs/s)
SGD classifier : 3887 train docs ( 438 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.957 in 2.61s ( 1489 docs/s)
Perceptron classifier : 3887 train docs ( 438 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.932 in 2.61s ( 1488 docs/s)
NB Multinomial classifier : 3887 train docs ( 438 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.912 in 2.64s ( 1473 docs/s)
Passive-Aggressive classifier : 3887 train docs ( 438 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.944 in 2.64s ( 1471 docs/s)
SGD classifier : 6322 train docs ( 723 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.963 in 4.21s ( 1500 docs/s)
Perceptron classifier : 6322 train docs ( 723 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.957 in 4.22s ( 1499 docs/s)
NB Multinomial classifier : 6322 train docs ( 723 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.922 in 4.25s ( 1489 docs/s)
Passive-Aggressive classifier : 6322 train docs ( 723 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.960 in 4.25s ( 1487 docs/s)
SGD classifier : 9213 train docs ( 1096 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.970 in 5.90s ( 1560 docs/s)
Perceptron classifier : 9213 train docs ( 1096 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.934 in 5.91s ( 1559 docs/s)
NB Multinomial classifier : 9213 train docs ( 1096 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.931 in 5.93s ( 1554 docs/s)
Passive-Aggressive classifier : 9213 train docs ( 1096 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.965 in 5.93s ( 1552 docs/s)
SGD classifier : 11557 train docs ( 1394 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.968 in 7.70s ( 1501 docs/s)
Perceptron classifier : 11557 train docs ( 1394 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.962 in 7.70s ( 1500 docs/s)
NB Multinomial classifier : 11557 train docs ( 1394 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.936 in 7.73s ( 1495 docs/s)
Passive-Aggressive classifier : 11557 train docs ( 1394 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.967 in 7.73s ( 1494 docs/s)
SGD classifier : 14352 train docs ( 1694 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.966 in 9.56s ( 1501 docs/s)
Perceptron classifier : 14352 train docs ( 1694 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.957 in 9.56s ( 1501 docs/s)
NB Multinomial classifier : 14352 train docs ( 1694 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.937 in 9.59s ( 1497 docs/s)
Passive-Aggressive classifier : 14352 train docs ( 1694 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.971 in 9.59s ( 1496 docs/s)
SGD classifier : 17191 train docs ( 2107 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.966 in 11.19s ( 1536 docs/s)
Perceptron classifier : 17191 train docs ( 2107 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.933 in 11.19s ( 1536 docs/s)
NB Multinomial classifier : 17191 train docs ( 2107 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.941 in 11.21s ( 1534 docs/s)
Passive-Aggressive classifier : 17191 train docs ( 2107 positive) 982 test docs ( 90 positive) accuracy: 0.973 in 11.21s ( 1533 docs/s)
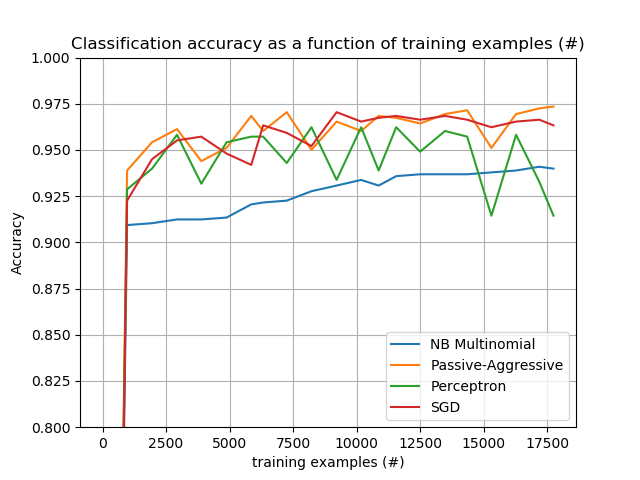
绘制结果
绘制分类器的学习曲线:小批次分类精度的演变。对前1000个样本进行精确性测量,并作为验证集进行检验。
为了限制内存消耗,在将样本输入给学习器之前,我们会将它们排到固定数量的队列中。
def plot_accuracy(x, y, x_legend):
"""Plot accuracy as a function of x."""
x = np.array(x)
y = np.array(y)
plt.title('Classification accuracy as a function of %s' % x_legend)
plt.xlabel('%s' % x_legend)
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.grid(True)
plt.plot(x, y)
rcParams['legend.fontsize'] = 10
cls_names = list(sorted(cls_stats.keys()))
# Plot accuracy evolution
plt.figure()
for _, stats in sorted(cls_stats.items()):
# Plot accuracy evolution with #examples
accuracy, n_examples = zip(*stats['accuracy_history'])
plot_accuracy(n_examples, accuracy, "training examples (#)")
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_ylim((0.8, 1))
plt.legend(cls_names, loc='best')
plt.figure()
for _, stats in sorted(cls_stats.items()):
# Plot accuracy evolution with runtime
accuracy, runtime = zip(*stats['runtime_history'])
plot_accuracy(runtime, accuracy, 'runtime (s)')
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_ylim((0.8, 1))
plt.legend(cls_names, loc='best')
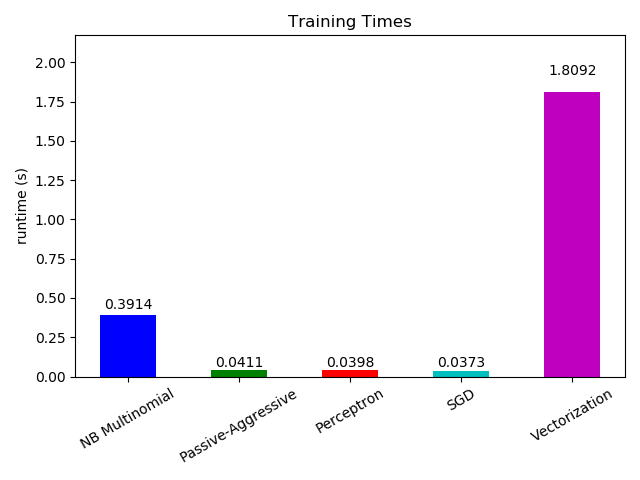
# Plot fitting times
plt.figure()
fig = plt.gcf()
cls_runtime = [stats['total_fit_time']
for cls_name, stats in sorted(cls_stats.items())]
cls_runtime.append(total_vect_time)
cls_names.append('Vectorization')
bar_colors = ['b', 'g', 'r', 'c', 'm', 'y']
ax = plt.subplot(111)
rectangles = plt.bar(range(len(cls_names)), cls_runtime, width=0.5,
color=bar_colors)
ax.set_xticks(np.linspace(0, len(cls_names) - 1, len(cls_names)))
ax.set_xticklabels(cls_names, fontsize=10)
ymax = max(cls_runtime) * 1.2
ax.set_ylim((0, ymax))
ax.set_ylabel('runtime (s)')
ax.set_title('Training Times')
def autolabel(rectangles):
"""attach some text vi autolabel on rectangles."""
for rect in rectangles:
height = rect.get_height()
ax.text(rect.get_x() + rect.get_width() / 2.,
1.05 * height, '%.4f' % height,
ha='center', va='bottom')
plt.setp(plt.xticks()[1], rotation=30)
autolabel(rectangles)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
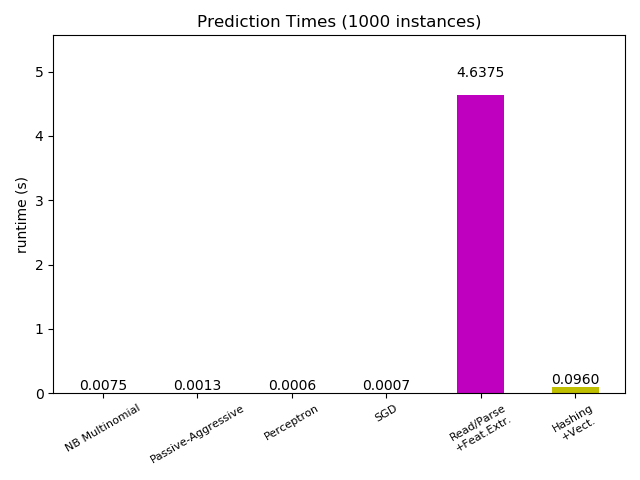
# Plot prediction times
plt.figure()
cls_runtime = []
cls_names = list(sorted(cls_stats.keys()))
for cls_name, stats in sorted(cls_stats.items()):
cls_runtime.append(stats['prediction_time'])
cls_runtime.append(parsing_time)
cls_names.append('Read/Parse\n+Feat.Extr.')
cls_runtime.append(vectorizing_time)
cls_names.append('Hashing\n+Vect.')
ax = plt.subplot(111)
rectangles = plt.bar(range(len(cls_names)), cls_runtime, width=0.5,
color=bar_colors)
ax.set_xticks(np.linspace(0, len(cls_names) - 1, len(cls_names)))
ax.set_xticklabels(cls_names, fontsize=8)
plt.setp(plt.xticks()[1], rotation=30)
ymax = max(cls_runtime) * 1.2
ax.set_ylim((0, ymax))
ax.set_ylabel('runtime (s)')
ax.set_title('Prediction Times (%d instances)' % n_test_documents)
autolabel(rectangles)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

脚本的总运行时间:(0分16.720秒)
Download Python source code:plot_out_of_core_classification.py
Download Jupyter notebook:plot_out_of_core_classification.ipynb




