使用Pipeline和GridSearchCV选择降维算法¶
本示例构建了一个进行降维处理,然后使用支持向量分类器进行预测的管道。 它演示了如何使用GridSearchCV和Pipeline在单个CV运行中优化不同类别的估计量–在网格搜索过程中,将无监督的PCA和NMF降维与单变量特征进行了比较。
此外,可以使用memory参数实例化管道,以记住管道内的转换器,从而避免反复安装相同的转换器。
请注意,当转换器的安装成本很高时,使用内存来启用缓存就变得很有趣。
管道和GridSearchCV的展示
本节说明了将Pipeline与GridSearchCV一起使用。
# 作者: Robert McGibbon, Joel Nothman, Guillaume Lemaitre
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA, NMF
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest, chi2
print(__doc__)
pipe = Pipeline([
# the reduce_dim stage is populated by the param_grid
('reduce_dim', 'passthrough'),
('classify', LinearSVC(dual=False, max_iter=10000))
])
N_FEATURES_OPTIONS = [2, 4, 8]
C_OPTIONS = [1, 10, 100, 1000]
param_grid = [
{
'reduce_dim': [PCA(iterated_power=7), NMF()],
'reduce_dim__n_components': N_FEATURES_OPTIONS,
'classify__C': C_OPTIONS
},
{
'reduce_dim': [SelectKBest(chi2)],
'reduce_dim__k': N_FEATURES_OPTIONS,
'classify__C': C_OPTIONS
},
]
reducer_labels = ['PCA', 'NMF', 'KBest(chi2)']
grid = GridSearchCV(pipe, n_jobs=1, param_grid=param_grid)
X, y = load_digits(return_X_y=True)
grid.fit(X, y)
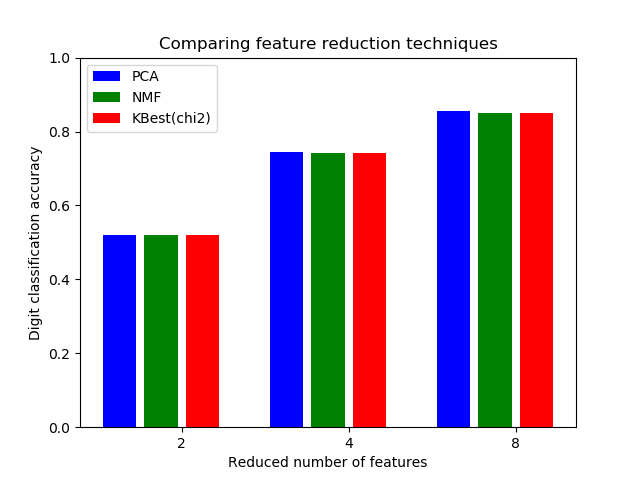
mean_scores = np.array(grid.cv_results_['mean_test_score'])
# 分数按param_grid迭代的顺序排列,按字母顺序排列
mean_scores = mean_scores.reshape(len(C_OPTIONS), -1, len(N_FEATURES_OPTIONS))
# 选择最佳C的分数
mean_scores = mean_scores.max(axis=0)
bar_offsets = (np.arange(len(N_FEATURES_OPTIONS)) *
(len(reducer_labels) + 1) + .5)
plt.figure()
COLORS = 'bgrcmyk'
for i, (label, reducer_scores) in enumerate(zip(reducer_labels, mean_scores)):
plt.bar(bar_offsets + i, reducer_scores, label=label, color=COLORS[i])
plt.title("Comparing feature reduction techniques")
plt.xlabel('Reduced number of features')
plt.xticks(bar_offsets + len(reducer_labels) / 2, N_FEATURES_OPTIONS)
plt.ylabel('Digit classification accuracy')
plt.ylim((0, 1))
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()
输出:
 在管道中缓存转换器
在管道中缓存转换器
有时值得存储特定转换器的状态,因为它可以再次使用。 在GridSearchCV中使用管道会触发这种情况。因此,我们使用参数内存(memory)来启用缓存。
警告:请注意,此示例仅是示例,因为在这种特定情况下,拟合PCA不一定比加载缓存慢。 因此,当转换器的安装成本很高时,请使用内存构造函数参数。
from joblib import Memory
from shutil import rmtree
# 创建一个临时文件夹来存储管道的转换器
location = 'cachedir'
memory = Memory(location=location, verbose=10)
cached_pipe = Pipeline([('reduce_dim', PCA()),
('classify', LinearSVC(dual=False, max_iter=10000))],
memory=memory)
# 这次,将在网格搜索中使用缓存的管道
# 退出前删除临时缓存
memory.clear(warn=False)
rmtree(location)
仅在评估LinearSVC分类器的C参数的第一配置时计算PCA拟合。 ‘C’的其他配置将触发缓存PCA估计器数据的加载,从而节省了处理时间。 因此,当安装转换器成本高昂时,使用内存对管道进行缓存非常有用。
脚本的总运行时间:(0分钟5.976秒)




