最近邻质心分类¶
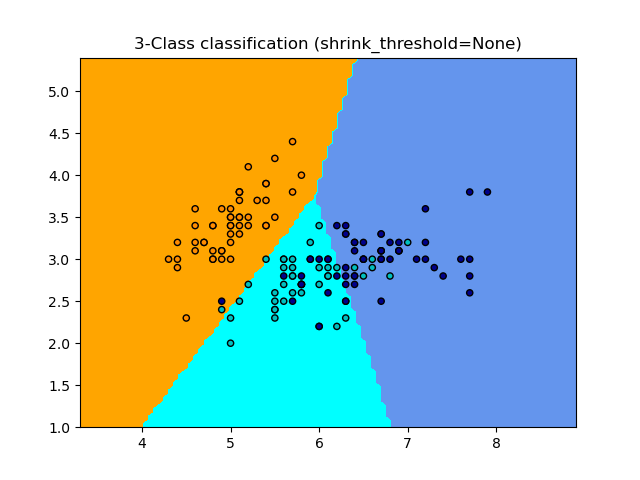
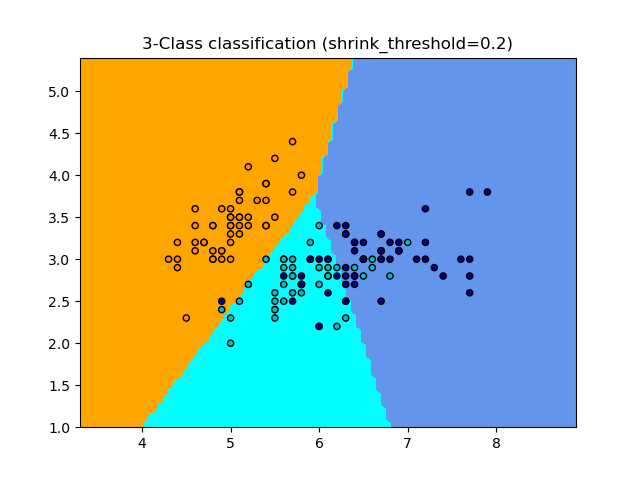
最近质心分类的样本用法。 本案例将绘制每个类别的决策边界。
输出:
None 0.8133333333333334
0.2 0.82
输入:
print(__doc__)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.neighbors import NearestCentroid
n_neighbors = 15
# 导入需要处理的数据
iris = datasets.load_iris()
# 我们仅采用前两个特征。我们可以通过使用二维数据集来避免使用复杂的切片
X = iris.data[:, :2]
y = iris.target
h = .02 # 设置网格中的步长
# 提取色谱
cmap_light = ListedColormap(['orange', 'cyan', 'cornflowerblue'])
cmap_bold = ListedColormap(['darkorange', 'c', 'darkblue'])
for shrinkage in [None, .2]:
# 我们创建最近邻分类器的实例并拟合数据。
clf = NearestCentroid(shrink_threshold=shrinkage)
clf.fit(X, y)
y_pred = clf.predict(X)
print(shrinkage, np.mean(y == y_pred))
# 绘制决策边界。为此,我们将为网格[x_min,x_max] x [y_min,y_max]中的每个点分配颜色。
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
# 将结果放入颜色图
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure()
plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cmap_light)
# 绘制训练数据
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap=cmap_bold,
edgecolor='k', s=20)
plt.title("3-Class classification (shrink_threshold=%r)"
% shrinkage)
plt.axis('tight')
plt.show()
脚本的总运行时间:(0分钟0.245秒)




