树森林的特征重要性¶
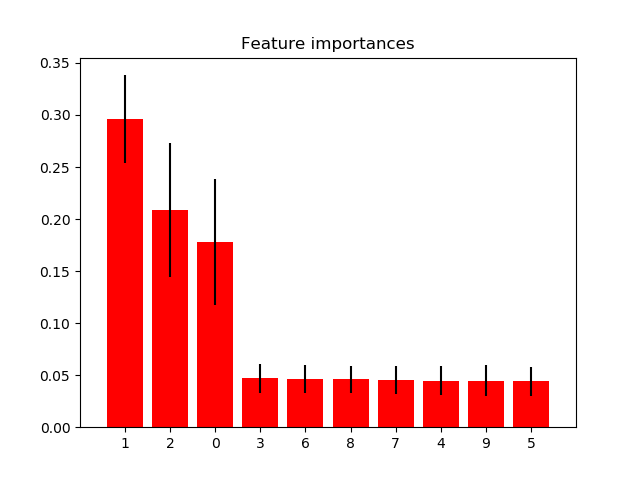
这个例子展示了如何利用树森林来评估特征在人工分类任务中的重要性。红色的柱子是森林以不存度为基础的特征重要性,也是树木间的差异。
正如预期的那样,图中显示了3个特征是信息丰富的,而其余的则不是。
警告:基于不存度的特征重要性可能会误导高基数特征(许多唯一的值)。参看sklearn.inspection.permutation_importance。
Feature ranking:
1. feature 1 (0.295902)
2. feature 2 (0.208351)
3. feature 0 (0.177632)
4. feature 3 (0.047121)
5. feature 6 (0.046303)
6. feature 8 (0.046013)
7. feature 7 (0.045575)
8. feature 4 (0.044614)
9. feature 9 (0.044577)
10. feature 5 (0.043912)
print(__doc__)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifier
# Build a classification task using 3 informative features
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000,
n_features=10,
n_informative=3,
n_redundant=0,
n_repeated=0,
n_classes=2,
random_state=0,
shuffle=False)
# Build a forest and compute the impurity-based feature importances
forest = ExtraTreesClassifier(n_estimators=250,
random_state=0)
forest.fit(X, y)
importances = forest.feature_importances_
std = np.std([tree.feature_importances_ for tree in forest.estimators_],
axis=0)
indices = np.argsort(importances)[::-1]
# Print the feature ranking
print("Feature ranking:")
for f in range(X.shape[1]):
print("%d. feature %d (%f)" % (f + 1, indices[f], importances[indices[f]]))
# Plot the impurity-based feature importances of the forest
plt.figure()
plt.title("Feature importances")
plt.bar(range(X.shape[1]), importances[indices],
color="r", yerr=std[indices], align="center")
plt.xticks(range(X.shape[1]), indices)
plt.xlim([-1, X.shape[1]])
plt.show()
脚本的总运行时间:(0分0.530秒)




