交叉分解法比较¶
注意 单击此处下载完整的示例代码,或通过Binder在浏览器中运行此示例
简单使用各种交叉分解算法: PLSCanonical - PLSRegression, 多变量响应, PLS2 - PLSRegression单变量响应, PLS1 - CCA。
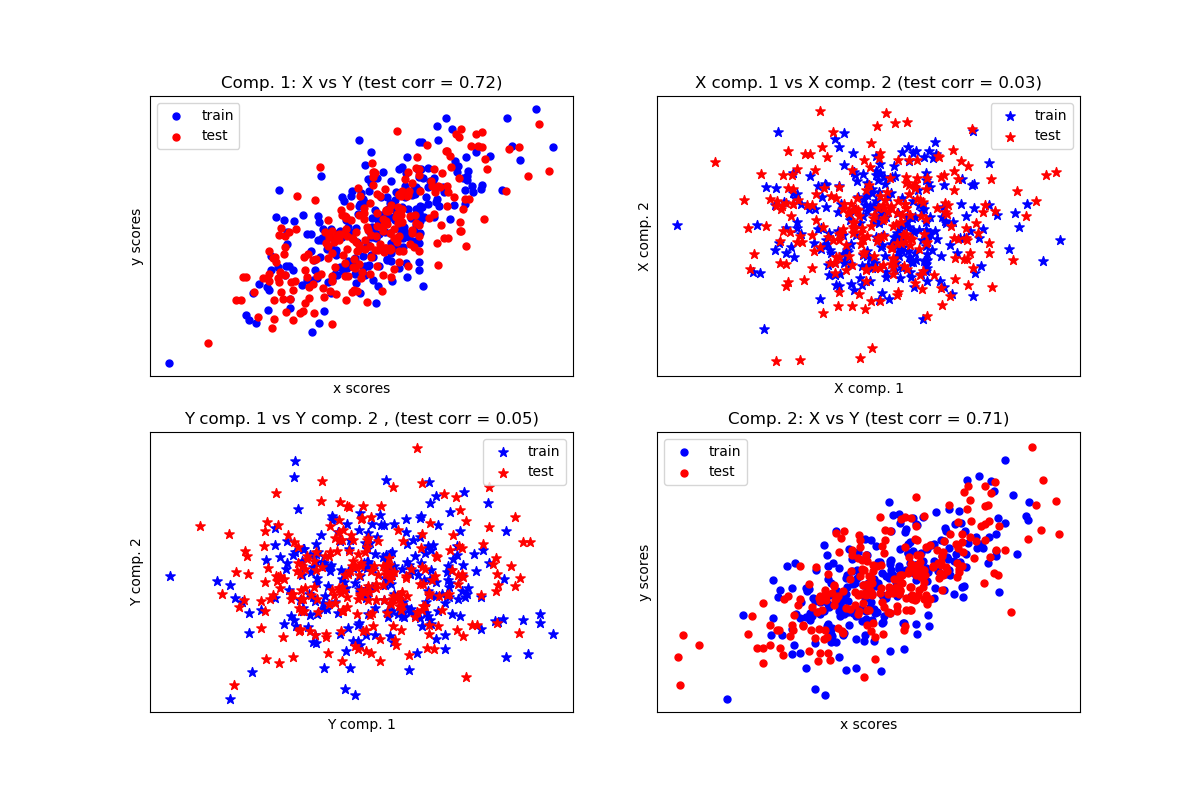
给定两个多元共变二维数据集X和Y,PLS提取协方差方向,即解释两个数据集之间最大共享方差的每个数据集的分量。这一点在散点矩阵图中有展示, 数据集X和数据集Y中的成分1是最大相关(点位于第一对角线周围)。这对于两个数据集中的成分2也是如此,但是,不同组件的数据集之间的相关性很弱:点云是非球面的。
Corr(X)
[[ 1. 0.51 0.07 -0.05]
[ 0.51 1. 0.11 -0.01]
[ 0.07 0.11 1. 0.49]
[-0.05 -0.01 0.49 1. ]]
Corr(Y)
[[1. 0.48 0.05 0.03]
[0.48 1. 0.04 0.12]
[0.05 0.04 1. 0.51]
[0.03 0.12 0.51 1. ]]
True B (such that: Y = XB + Err)
[[1 1 1]
[2 2 2]
[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]]
Estimated B
[[ 1. 1. 1. ]
[ 2. 2. 2. ]
[-0. -0. 0. ]
[ 0. 0. 0. ]
[ 0. 0. 0. ]
[ 0. 0. -0. ]
[-0. -0. -0.1]
[-0. -0. 0. ]
[ 0. 0. 0.1]
[ 0. 0. -0. ]]
Estimated betas
[[ 1. ]
[ 2.1]
[ 0. ]
[ 0. ]
[ 0. ]
[-0. ]
[-0. ]
[ 0. ]
[-0. ]
[-0. ]]
print(__doc__)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cross_decomposition import PLSCanonical, PLSRegression, CCA
# #############################################################################
# Dataset based latent variables model
n = 500
# 2 latents vars:
l1 = np.random.normal(size=n)
l2 = np.random.normal(size=n)
latents = np.array([l1, l1, l2, l2]).T
X = latents + np.random.normal(size=4 * n).reshape((n, 4))
Y = latents + np.random.normal(size=4 * n).reshape((n, 4))
X_train = X[:n // 2]
Y_train = Y[:n // 2]
X_test = X[n // 2:]
Y_test = Y[n // 2:]
print("Corr(X)")
print(np.round(np.corrcoef(X.T), 2))
print("Corr(Y)")
print(np.round(np.corrcoef(Y.T), 2))
# #############################################################################
# Canonical (symmetric) PLS
# Transform data
# ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
plsca = PLSCanonical(n_components=2)
plsca.fit(X_train, Y_train)
X_train_r, Y_train_r = plsca.transform(X_train, Y_train)
X_test_r, Y_test_r = plsca.transform(X_test, Y_test)
# Scatter plot of scores
# ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
# 1) On diagonal plot X vs Y scores on each components
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.subplot(221)
plt.scatter(X_train_r[:, 0], Y_train_r[:, 0], label="train",
marker="o", c="b", s=25)
plt.scatter(X_test_r[:, 0], Y_test_r[:, 0], label="test",
marker="o", c="r", s=25)
plt.xlabel("x scores")
plt.ylabel("y scores")
plt.title('Comp. 1: X vs Y (test corr = %.2f)' %
np.corrcoef(X_test_r[:, 0], Y_test_r[:, 0])[0, 1])
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.subplot(224)
plt.scatter(X_train_r[:, 1], Y_train_r[:, 1], label="train",
marker="o", c="b", s=25)
plt.scatter(X_test_r[:, 1], Y_test_r[:, 1], label="test",
marker="o", c="r", s=25)
plt.xlabel("x scores")
plt.ylabel("y scores")
plt.title('Comp. 2: X vs Y (test corr = %.2f)' %
np.corrcoef(X_test_r[:, 1], Y_test_r[:, 1])[0, 1])
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.legend(loc="best")
# 2) Off diagonal plot components 1 vs 2 for X and Y
plt.subplot(222)
plt.scatter(X_train_r[:, 0], X_train_r[:, 1], label="train",
marker="*", c="b", s=50)
plt.scatter(X_test_r[:, 0], X_test_r[:, 1], label="test",
marker="*", c="r", s=50)
plt.xlabel("X comp. 1")
plt.ylabel("X comp. 2")
plt.title('X comp. 1 vs X comp. 2 (test corr = %.2f)'
% np.corrcoef(X_test_r[:, 0], X_test_r[:, 1])[0, 1])
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.subplot(223)
plt.scatter(Y_train_r[:, 0], Y_train_r[:, 1], label="train",
marker="*", c="b", s=50)
plt.scatter(Y_test_r[:, 0], Y_test_r[:, 1], label="test",
marker="*", c="r", s=50)
plt.xlabel("Y comp. 1")
plt.ylabel("Y comp. 2")
plt.title('Y comp. 1 vs Y comp. 2 , (test corr = %.2f)'
% np.corrcoef(Y_test_r[:, 0], Y_test_r[:, 1])[0, 1])
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.show()
# #############################################################################
# PLS regression, with multivariate response, a.k.a. PLS2
n = 1000
q = 3
p = 10
X = np.random.normal(size=n * p).reshape((n, p))
B = np.array([[1, 2] + [0] * (p - 2)] * q).T
# each Yj = 1*X1 + 2*X2 + noize
Y = np.dot(X, B) + np.random.normal(size=n * q).reshape((n, q)) + 5
pls2 = PLSRegression(n_components=3)
pls2.fit(X, Y)
print("True B (such that: Y = XB + Err)")
print(B)
# compare pls2.coef_ with B
print("Estimated B")
print(np.round(pls2.coef_, 1))
pls2.predict(X)
# PLS regression, with univariate response, a.k.a. PLS1
n = 1000
p = 10
X = np.random.normal(size=n * p).reshape((n, p))
y = X[:, 0] + 2 * X[:, 1] + np.random.normal(size=n * 1) + 5
pls1 = PLSRegression(n_components=3)
pls1.fit(X, y)
# note that the number of components exceeds 1 (the dimension of y)
print("Estimated betas")
print(np.round(pls1.coef_, 1))
# #############################################################################
# CCA (PLS mode B with symmetric deflation)
cca = CCA(n_components=2)
cca.fit(X_train, Y_train)
X_train_r, Y_train_r = cca.transform(X_train, Y_train)
X_test_r, Y_test_r = cca.transform(X_test, Y_test)
脚本的总运行时间:(0分0.237秒)
Download Python source code: plot_compare_cross_decomposition.py
Download Jupyter notebook: plot_compare_cross_decomposition.ipynb




